Dioxolane: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
{{chemistry-stub}} | {{chemistry-stub}} | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
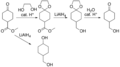
File:Dioxolane_synthesis.png|Dioxolane synthesis | |||
File:Acetal-protection-example.png|Acetal protection example | |||
File:Neosporol_epoxidation-rearrangement.png|Neosporol epoxidation rearrangement | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:48, 18 February 2025
Dioxolane is a heterocyclic compound that is classified as a saturated ether. It is a colorless liquid and is used as a solvent, as well as in the production of polymers and pharmaceuticals.
Structure and Properties[edit]
Dioxolane is a five-membered ring compound, with two oxygen atoms and three carbon atoms in the ring. The molecular formula of dioxolane is C3H6O2. It is a type of cyclic ether, also known as an epoxide.
The structure of dioxolane is similar to that of dioxane, but with one less carbon atom in the ring. This results in a more strained and less stable structure, which can affect its reactivity and other properties.
Uses[edit]
Dioxolane is used as a solvent in various industrial applications, due to its ability to dissolve a wide range of organic compounds. It is also used in the production of polymers, where it can act as a chain transfer agent.
In the pharmaceutical industry, dioxolane is used in the synthesis of certain drugs. For example, it is used in the production of artemisinin, a drug used to treat malaria.
Safety and Environmental Impact[edit]
Like many organic solvents, dioxolane can be harmful if inhaled, ingested, or comes into contact with the skin. It is also flammable, and can react with strong oxidizing agents.
The environmental impact of dioxolane is not well-studied, but it is known to be biodegradable and is not expected to bioaccumulate. However, like all chemicals, it should be handled and disposed of properly to minimize its impact on the environment.
See Also[edit]
-
Dioxolane synthesis
-
Acetal protection example
-
Neosporol epoxidation rearrangement