Young worker safety and health
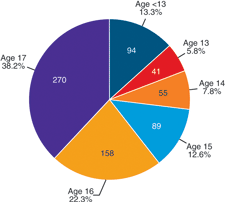
Young Worker Safety and Health is a critical area of focus within the fields of occupational safety and health and labor rights. It pertains to the laws, regulations, and practices designed to protect individuals under the age of 18 in the workforce. Given their inexperience and the developmental stage, young workers are at a higher risk for workplace injuries and exploitation. This article explores the key aspects of young worker safety and health, including legal protections, common hazards, and strategies for ensuring their well-being in the workplace.
Legal Protections[edit]
In many countries, specific laws and regulations are designed to provide special protections for young workers. These laws often include restrictions on the types of work young people can perform, the hours they can work, and the conditions under which they can work.
United States[edit]
In the United States, the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) sets the age minimums for employment and limits the number of hours minors can work. It also restricts the employment of minors in certain hazardous occupations. Additionally, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) enforces regulations that protect young workers from workplace hazards.
International[edit]
Globally, the International Labour Organization (ILO) advocates for the rights of young workers, including the minimum age for employment and protection from hazardous work through conventions such as C138 (Minimum Age Convention) and C182 (Worst Forms of Child Labour Convention).
Common Hazards[edit]
Young workers are often employed in sectors such as retail, food service, agriculture, and construction, where they may be exposed to various hazards. These include:
- Physical hazards: such as operating heavy machinery or lifting heavy objects.
- Chemical hazards: exposure to toxic substances.
- Biological hazards: exposure to infectious diseases, especially in healthcare settings.
- Psychosocial hazards: including stress and harassment.
Prevention and Education[edit]
Preventing workplace injuries and illnesses among young workers involves a combination of education, training, and enforcement of safety standards. Employers play a crucial role in providing a safe working environment and adequate training on how to perform tasks safely. Additionally, schools and community organizations can offer programs to educate young people about their rights and how to protect themselves at work.
Conclusion[edit]
Ensuring the safety and health of young workers is essential for their physical and psychological well-being, as well as for fostering a productive and ethical working environment. It requires the concerted efforts of governments, employers, workers, and society as a whole to uphold the rights of young workers and protect them from harm.
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


