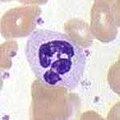
Wright's stain
Wright's stain is a histological stain that facilitates the differentiation of blood cell types. It is a commonly used stain in both hematology and the study of blood and bone marrow specimens. The stain is named after James Homer Wright, who devised the stain at the end of the 19th century. Wright's stain is a combination of eosin (a red dye) and methylene blue in methanol, which, when applied to a blood smear, yields distinct colors for different types of cells, allowing for their identification and study.
Composition and Mechanism[edit]
Wright's stain works through the principle of acid-base staining. Eosin is acidic and stains basic (or alkaline) components of the cells, such as the cytoplasm, a pink or red color. Methylene blue is basic and stains acidic components, such as nucleic acids within the nucleus, a blue or purple color. This differential staining reveals detailed structures within the cells, such as the nucleus, cytoplasm, and granules, making it easier to distinguish between different types of blood cells.
Procedure[edit]
The staining procedure involves preparing a thin film of blood on a slide, which is then fixed with methanol. The Wright's stain is applied for a specific time, followed by a rinse with a buffered water solution. The slide is then dried and can be examined under a microscope. The specific timing and concentration of the stain and buffer solution can vary, and optimal results may require adjustment based on specific laboratory conditions.
Applications[edit]
Wright's stain is extensively used in the field of hematology for performing a Complete Blood Count (CBC) and differential blood count. This staining technique allows for the identification and enumeration of different types of blood cells, including erythrocytes (red blood cells), leukocytes (white blood cells), and platelets. It is particularly useful in diagnosing blood disorders, such as anemia, leukemia, and infections, by revealing abnormalities in blood cell size, shape, and number.
Types of Cells Identified[edit]
- Erythrocytes: Appear as pink or red discs without a nucleus.
- Leukocytes:
- Neutrophils: Show a multi-lobed nucleus and light pink granules.
- Lymphocytes: Have a large, round nucleus with a thin rim of cytoplasm.
- Monocytes: Feature a large, kidney-shaped nucleus.
- Eosinophils: Contain bright red-orange granules.
- Basophils: Display dark purple-black granules.
- Platelets: Appear as small, darkly stained fragments.
Advantages and Limitations[edit]
Wright's stain offers the advantage of providing detailed visualization of blood cells, which is crucial for diagnosing various hematological conditions. However, its effectiveness can be influenced by the quality of the blood smear, the precise formulation of the stain, and the staining procedure. Variations in these factors can lead to inconsistent results, making it essential for laboratory personnel to be skilled in the technique and for standard operating procedures to be in place.
Wright's stain[edit]
-
Wright's staining of multiple myeloma, plasmablastic type
-
Lymphocyte
-
Basophil
-
Neutrophil
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian