Tsunami
Tsunami[edit]
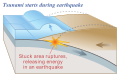
A tsunami is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and other underwater explosions (including detonations, landslides, glacier calvings, meteorite impacts, and other disturbances above or below water) all have the potential to generate a tsunami. Unlike normal ocean waves, which are generated by wind or tides, a tsunami is characterized by its long wavelength, which can be hundreds of kilometers long.
Etymology[edit]
The term "tsunami" is a Japanese word, with the characters _ (tsu) meaning "harbor" and _ (nami) meaning "wave." The term was adopted into English to describe the phenomenon of large sea waves caused by underwater seismic activity.
Causes[edit]
Tsunamis are primarily caused by underwater earthquakes, which occur when tectonic plates shift abruptly and displace the water above. Other causes include volcanic eruptions, underwater landslides, and meteorite impacts. The sudden displacement of water generates waves that travel across the ocean at high speeds.
Characteristics[edit]
Tsunamis have a small wave height offshore, and a very long wavelength (often hundreds of kilometers long), which is why they generally pass unnoticed at sea, forming only a slight swell usually about 300 millimeters (12 in) above the normal sea surface. As the tsunami approaches land, the wave height increases dramatically.
Historical Tsunamis[edit]
One of the most devastating tsunamis in recorded history occurred on December 26, 2004, in the Indian Ocean. Triggered by a massive undersea earthquake off the coast of Sumatra, Indonesia, the tsunami affected 14 countries and resulted in over 230,000 deaths. Another significant event was the 1755 Lisbon earthquake, which generated a tsunami that struck the coasts of Portugal, Spain, and North Africa.
Detection and Warning Systems[edit]
Modern tsunami warning systems use a combination of seismic data and sea-level monitoring to detect tsunamis. These systems are designed to provide early warnings to coastal areas, allowing for evacuation and other safety measures to be implemented.
Mitigation and Preparedness[edit]
Coastal communities in tsunami-prone areas often have evacuation routes and signage to guide residents to higher ground. Structures such as tsunami walls are also constructed to protect against the impact of waves.
Related Pages[edit]
References[edit]
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). "Tsunami." Retrieved from [1]
- United States Geological Survey (USGS). "Tsunami and Earthquake Research." Retrieved from [2]
Gallery[edit]
-
2004 Indian Ocean tsunami
-
Animation of tsunami propagation
-
Aftermath in Aceh, Indonesia
-
1755 Lisbon earthquake and tsunami
-
Diagram of tsunami generation
-
Diagram of tsunami propagation
-
Diagram of tsunami impact
-
Diagram of tsunami run-up
-
Tsunami wave
-
Tsunami impact
-
Tsunami aftermath
-
Tsunami propagation in variable depth
-
Tsunami wave
-
Shallow water wave
-
Tsunami run-up and inundation
-
Travel time map for 1964 Alaska tsunami
-
Tsunami hazard zone sign
-
Tsunami warning sign in Japan
-
Inundation zone sign
-
Tsunami evacuation route sign
-
DART tsunami detection system
-
Tsunami wall
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian