Tram
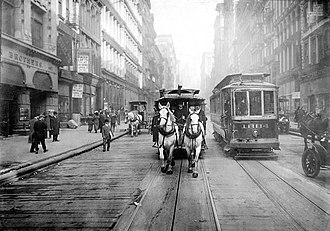
Tram refers to a form of public transport that runs on tracks embedded in city streets or on separate rights-of-way. It is also known as a streetcar or trolley in some regions. Trams are a popular mode of transportation in many cities around the world due to their capacity, reliability, and eco-friendliness compared to other forms of urban transport.
History[edit]
The first tram services were horse-drawn and began operation in the early 19th century. The Swansea and Mumbles Railway in Wales, UK, is recorded as the world's first passenger tram service, starting in 1807. With the advent of electricity, the late 19th century saw the electrification of tram systems, significantly improving their efficiency and capacity. This transition marked the beginning of the modern tram era, with the first electric tram service starting in Saratov, Russia, in 1880.
Operation[edit]
Trams are powered by electricity, typically supplied through overhead lines. They run on tracks that are either embedded in the road surface shared with other vehicles or on dedicated tracks. Some tram systems, known as light rail, have segments that run on tracks separated from road traffic, allowing for higher speeds.
Trams are known for their ability to transport a large number of passengers while occupying less road space compared to buses. They are considered a more environmentally friendly option due to their electric power source and the reduction of road congestion they can contribute to.
Types of Trams[edit]
There are several types of trams, including:
- Classic Trams: Traditional street-running vehicles, often found in historic city centers.
- Modern Low-Floor Trams: These trams have low floors for easy access, improving accessibility for passengers with mobility issues.
- Articulated Trams: Longer trams with flexible sections, allowing them to carry more passengers.
- Heritage Trams: Historic trams preserved for tourist or nostalgic purposes, often running in conjunction with modern services.
Advantages and Disadvantages[edit]
Advantages[edit]
- High passenger capacity
- Environmentally friendly
- Can reduce urban congestion
- Provides reliable and frequent service
Disadvantages[edit]
- High initial infrastructure and maintenance costs
- Can be slower than other forms of transport due to sharing road space in some areas
- Requires dedicated tracks and overhead lines, which can impact the aesthetics of city streets
Future of Trams[edit]
The future of trams looks promising, with many cities investing in new tram lines or upgrading existing ones. Innovations such as battery-powered trams and the integration of tram systems with other forms of public transport are making trams more versatile and environmentally friendly. As cities continue to grow and seek sustainable transport solutions, trams are likely to play a key role in urban transport strategies.
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
