Thogotovirus
Thogotovirus is a genus of viruses within the family Orthomyxoviridae, which is known for containing viruses that primarily infect vertebrate hosts, including humans and other mammals, as well as invertebrates such as ticks and mosquitoes. Thogotoviruses are arboviruses, meaning they are transmitted by arthropod vectors. The genus includes several species, with Thogoto virus and Dhori virus being among the most studied due to their potential to cause disease in humans and animals.
Structure and Genome[edit]
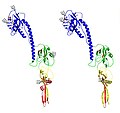
Thogotoviruses are enveloped viruses with a segmented, single-stranded, negative-sense RNA genome. The genome typically consists of six segments, encoding for at least six proteins, including the surface glycoproteins involved in virus attachment to host cells, and the internal proteins responsible for viral replication and assembly. The structure of Thogotoviruses is similar to other members of the Orthomyxoviridae family, featuring a spherical to pleomorphic shape with a diameter ranging from 80 to 120 nm.
Transmission and Epidemiology[edit]
Thogotoviruses are transmitted to vertebrates through the bite of infected arthropods, primarily ticks and mosquitoes. The distribution of Thogotoviruses is worldwide, with specific viruses having been identified in various geographical locations, including Africa, Asia, Europe, and North America. The prevalence and incidence of Thogotovirus infections in humans and animals are not well-documented, partly due to the lack of widespread surveillance and the non-specific nature of the symptoms associated with infection.
Pathogenesis and Clinical Features[edit]
In humans, Thogotovirus infections can range from asymptomatic to causing flu-like symptoms, such as fever, fatigue, muscle aches, and headaches. Severe cases, although rare, can lead to encephalitis, meningitis, or hemorrhagic fever, posing significant health risks. The pathogenesis of Thogotovirus infections involves the virus entering the host through the skin, followed by replication in local tissues and dissemination to various organs, including the central nervous system in severe cases.
Diagnosis and Treatment[edit]
Diagnosis of Thogotovirus infections is primarily based on the detection of viral RNA, antibodies against the virus, or virus isolation from clinical specimens. Molecular techniques such as reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) are commonly used for viral RNA detection. Treatment is mainly supportive, focusing on the management of symptoms, as there are no specific antiviral therapies approved for Thogotovirus infections. Prevention strategies include avoiding bites from ticks and mosquitoes and controlling vector populations.
Research and Future Directions[edit]
Research on Thogotoviruses is ongoing, with studies focusing on understanding the virus's molecular biology, pathogenesis, and interactions with both vertebrate hosts and invertebrate vectors. The development of vaccines and specific antiviral treatments against Thogotoviruses is an area of interest, given the potential for these viruses to cause disease in humans and animals. Additionally, surveillance and research efforts are aimed at identifying new Thogotovirus species and understanding their epidemiology and potential impact on public health.
-
Thogotovirus
-
Thogotovirus virion
-
Thogotovirus genomes
-
Thogotovirus glycoprotein comparison
-
Thogotovirus
-
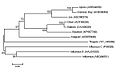
Thogotovirus phylogeny
-
Hyalomma marginatum
-
Thogotovirus
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian