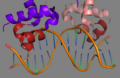
TetR
Tetracycline (often abbreviated as Tc) belongs to a broad spectrum of antibiotics recognized for their role in treating a variety of bacterial infections. Over time, however, many bacterial strains have developed resistance to tetracycline, largely mediated through the expression of specific resistance genes. Central to the regulation of these genes is the Tet Repressor Protein, commonly referred to as TetR. Beyond its natural biological role, TetR has been co-opted for a range of biotechnological applications, particularly in the realm of artificially engineered gene regulatory networks.
Tetracycline: The Antibiotic[edit]
Tetracycline exerts its antibacterial effect by inhibiting protein synthesis in susceptible bacteria. It achieves this by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit, thereby preventing the attachment of aminoacyl-tRNA to the bacterial ribosome during protein synthesis<ref>Chopra, I., & Roberts, M. (2001). Tetracycline antibiotics: mode of action, applications, molecular biology, and epidemiology of bacterial resistance. Microbiology and molecular biology reviews, 65(2), 232-260.</ref>.
Resistance to Tetracycline[edit]
Bacteria have developed multiple mechanisms to resist the action of tetracycline. One of the primary methods involves the expression of genes that encode for efflux pumps or ribosomal protection proteins<ref>Thaker, M., Spanogiannopoulos, P., & Wright, G. D. (2010). The tetracycline resistome. Cell and molecular life sciences, 67(3), 419-431.</ref>. The expression of these resistance genes is tightly controlled by the Tet Repressor Protein (TetR).
Tet Repressor Protein (TetR): TetR is a regulatory protein that binds to the operator regions of Tc resistance genes, inhibiting their expression. When tetracycline is present, it binds to TetR, causing a conformational change in the repressor protein that reduces its affinity for the operator, thereby allowing the expression of the resistance genes<ref>Ramos, J. L., Martínez-Bueno, M., Molina-Henares, A. J., Terán, W., Watanabe, K., Zhang, X., ... & Tobes, R. (2005). The TetR family of transcriptional repressors. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 69(2), 326-356.</ref>.
TetR in Synthetic Biology[edit]
Owing to its unique regulatory properties, TetR has found applications in the field of synthetic biology. Its capability for fine-tuned regulation makes it an ideal candidate for creating controllable genetic circuits.
Artificial Gene Regulatory Networks: TetR's responsiveness to minute concentrations of tetracycline makes it suitable for designing feedback loops and other regulatory mechanisms. By harnessing the TetR system, researchers can achieve precise control over gene expression in response to specific external stimuli. Use in Cloning Vectors: The E. coli cloning vector pBR322, a cornerstone in molecular biology, contains the TetR gene. This not only provides resistance to tetracycline but also serves as a selectable marker for successful cloning events<ref>Sutcliffe, J. G. (1978). Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harbor symposia on quantitative biology, 43, 77-90.</ref>.
Conclusion[edit]
The interplay between tetracycline and the Tet Repressor Protein underscores the evolutionary battle between antibiotics and bacteria. While resistance mechanisms challenge the clinical utility of antibiotics, they also provide tools for scientific discovery and biotechnological innovations. TetR's dual role, both in mediating resistance and in advancing synthetic biology, highlights the importance of understanding these biological systems in depth.
See also Tetracycline controlled transcriptional activation
External links[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
| This article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by registering to expand it. |
-
Overview of TetR
-
TetR in complex with TcMg
-
TetR bound to DNA
-
HTH alignment of 3 TetR family members
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian