Tanning lamp
Tanning lamp refers to an artificial light source designed to produce ultraviolet (UV) radiation, mimicking the sun's effect on the skin to induce a cosmetic tan. Primarily found in tanning beds or booths, these lamps facilitate skin tanning by emitting UV radiation, which stimulates melanin production in the skin. The use of tanning lamps has been both popular for aesthetic reasons and controversial due to health concerns.
Types of Tanning Lamps[edit]
Tanning lamps can be categorized based on the UV radiation they emit:
- UVA Lamps: Emit long-wave UVA radiation, which penetrates deeper into the skin but is less likely to cause immediate sunburn. UVA lamps are often marketed as "safer" or "bronzing."
- UVB Lamps: Emit short-wave UVB radiation, more closely associated with sunburn but also more effective at stimulating vitamin D production. UVB lamps are typically used for medical treatments, such as psoriasis.
- Combination UVA/UVB Lamps: Provide a mix of UVA and UVB radiation, aiming to balance the tanning effect with a reduced risk of sunburn.
Health Risks and Benefits[edit]
The use of tanning lamps is associated with several health risks and benefits:
Risks[edit]
- Skin Cancer: Prolonged exposure to UV radiation increases the risk of developing skin cancers, including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma.
- Premature Aging: UV radiation can lead to premature skin aging, characterized by wrinkles, leathery skin, and age spots.
- Eye Damage: Without proper eye protection, exposure to UV radiation can harm the eyes, leading to conditions such as cataracts.
Benefits[edit]
- Vitamin D Synthesis: UVB radiation from tanning lamps can promote vitamin D synthesis in the skin, which is essential for bone health and immune function.
- Psoriasis Treatment: UVB lamps are used in phototherapy to treat psoriasis, a condition that causes skin cells to multiply rapidly, leading to scaly patches.
Regulation and Safety[edit]
Due to the health risks associated with UV radiation, the use of tanning lamps is regulated in many countries. Regulations may include age restrictions, mandatory protective eyewear, and limits on exposure time. It is crucial for users to follow safety guidelines to minimize health risks.
Alternatives[edit]
For those seeking a tan without the risks associated with UV radiation, alternatives include:
- Sunless Tanning Products: Lotions, sprays, and gels that temporarily stain the skin.
- Spray Tanning: A professional service that applies a fine mist of sunless tanning solution to the skin.
Conclusion[edit]
While tanning lamps offer a convenient way to achieve a cosmetic tan, it is important to weigh the aesthetic benefits against the potential health risks. Users should consider safer alternatives and adhere to safety guidelines when using tanning lamps.
-
Tanning lamp
-
End of a tanning lamp
-
Ultraviolet tanning bed lamp running
-
High pressure tanning bulb
-
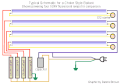
Choke ballast for tanning lamp
-
Starter for tanning lamp
-
Choke ballast diagram
-
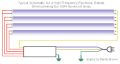
High frequency ballast diagram
-
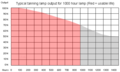
Lamp output graph
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian