Second Bulgarian Empire


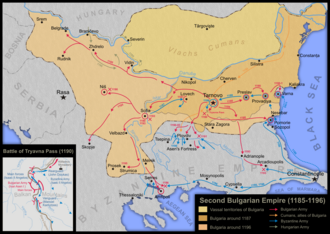




The Second Bulgarian Empire (Template:Lang-bg, Vtoro Balgarsko Tsarstvo) was a medieval Bulgarian state that existed between 1185 and 1396. It emerged as a result of the Uprising of Asen and Peter against the Byzantine Empire and was eventually conquered by the Ottoman Empire.
History[edit]
Foundation[edit]
The Second Bulgarian Empire was founded in 1185 following the successful Uprising of Asen and Peter led by the brothers Ivan Asen I and Peter IV. The rebellion was sparked by heavy taxation imposed by the Byzantine Emperor Isaac II Angelos.
Expansion and Golden Age[edit]
Under the rule of Kaloyan (1197–1207) and Ivan Asen II (1218–1241), the empire expanded significantly. Kaloyan achieved a notable victory against the Latin Empire at the Battle of Adrianople in 1205. Ivan Asen II's reign is often considered the Golden Age of the Second Bulgarian Empire, marked by territorial expansion, economic prosperity, and cultural achievements.
Decline[edit]
The decline of the empire began in the late 13th century due to internal strife, invasions by the Golden Horde, and the rise of the Serbian Empire. The final blow came with the Ottoman invasions in the late 14th century. The empire was eventually conquered in 1396, marking the end of Bulgarian independence until the late 19th century.
Culture[edit]
The Second Bulgarian Empire was a center of Eastern Orthodox Christianity and Old Bulgarian culture. The capital, Tarnovo, became a major cultural and religious center, often referred to as the "Third Rome."
Economy[edit]
The economy of the Second Bulgarian Empire was based on agriculture, trade, and crafts. The empire controlled important trade routes connecting Europe and Asia, which contributed to its economic prosperity.
Legacy[edit]
The Second Bulgarian Empire left a lasting legacy in the history of Bulgaria and the Balkans. It played a crucial role in the preservation and development of Eastern Orthodox Christianity and Old Bulgarian culture.
Related Pages[edit]
- First Bulgarian Empire
- Byzantine Empire
- Ottoman Empire
- Tarnovo
- Ivan Asen I
- Ivan Asen II
- Kaloyan of Bulgaria
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian