Scallop aquaculture




Scallop aquaculture refers to the process of cultivating and harvesting scallops in a controlled environment, as opposed to capturing them in the wild. This form of aquaculture is a significant part of the seafood industry, providing a sustainable source of scallops for consumption. Scallop farming has been developed due to the increasing demand for scallops and concerns over the sustainability of wild scallop populations.
History[edit]
The history of scallop aquaculture dates back to the early 20th century, with Japan being one of the pioneers in the field. The practice has since spread to various parts of the world, including North America, Europe, and China, each region adapting different techniques suitable for their local conditions.
Species[edit]
Several species of scallops are cultivated, including the Pacific scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis), the Atlantic sea scallop (Placopecten magellanicus), and the King scallop (Pecten maximus). The choice of species depends on the environmental conditions and market demands.
Cultivation Methods[edit]
Scallop aquaculture can be carried out using various methods, including:
- Bottom Culture: Scallops are grown directly on the seabed. This method is similar to how wild scallops live but allows for easier monitoring and management.
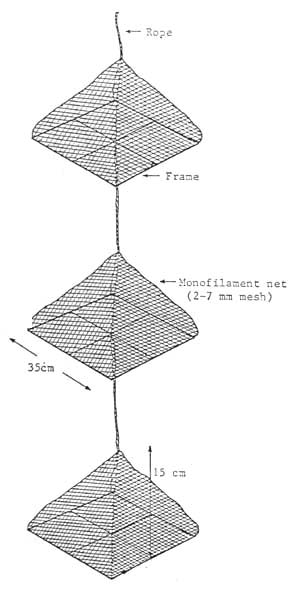
- Suspended Culture: Scallops are grown in nets, cages, or lanterns suspended in the water column. This method promotes faster growth rates and reduces the risk of predation and disease.
- Ear Hanging: A technique where scallops are suspended by drilling a small hole near the hinge of the shell and attaching them to a line. This method maximizes space and allows for individual growth monitoring.
Environmental Impact[edit]
Scallop aquaculture has a relatively low environmental impact compared to other forms of aquaculture. Scallops filter feed on plankton, which means they do not require feed inputs, reducing the risk of pollution from uneaten feed. However, the structures used for suspended cultures can alter local ecosystems, and there is a risk of genetic pollution if farmed scallops interbreed with wild populations.
Economic Importance[edit]
The cultivation of scallops provides economic benefits to coastal communities, offering employment opportunities and a source of income. Scallop aquaculture also contributes to the seafood industry by providing a consistent and sustainable supply of scallops.
Challenges[edit]
Despite its benefits, scallop aquaculture faces several challenges, including vulnerability to diseases, the impact of climate change on water temperatures and ocean acidity, and the need for improvements in hatchery technologies to ensure a stable supply of seed scallops.
Future Directions[edit]
Research in scallop aquaculture is focused on improving hatchery techniques, developing more sustainable and efficient cultivation methods, and understanding the impacts of climate change on scallop populations. Advances in genetics and breeding programs are also promising for enhancing disease resistance and growth rates.
| This article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by registering to expand it. |
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian