SARS-related coronavirus
Group of viruses related to SARS-CoV

SARS-related coronavirus is a species of coronavirus that includes the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, which is responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. These viruses belong to the genus Betacoronavirus and the subgenus Sarbecovirus.
Virology[edit]
SARS-related coronaviruses are enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses. They are characterized by their crown-like appearance under an electron microscope, which is due to the presence of spike glycoproteins on their surface.
Genome[edit]

The genome of SARS-related coronaviruses is approximately 30 kilobases in length, making it one of the largest among RNA viruses. The genome encodes several structural proteins, including the spike (S), envelope (E), membrane (M), and nucleocapsid (N) proteins, as well as non-structural proteins involved in viral replication.
Phylogenetics[edit]

Phylogenetic studies have shown that SARS-related coronaviruses are closely related to other bat coronaviruses, suggesting a zoonotic origin. The viruses are believed to have originated in bats and may have been transmitted to humans through intermediate hosts.
Pathogenesis[edit]
SARS-related coronaviruses primarily infect the respiratory tract, leading to symptoms ranging from mild respiratory illness to severe pneumonia. The viruses can cause acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and have a high mortality rate in severe cases.
Transmission[edit]
The primary mode of transmission for SARS-related coronaviruses is through respiratory droplets. The viruses can also spread through contact with contaminated surfaces and, in some cases, through aerosols.
Replication Cycle[edit]

The replication cycle of SARS-related coronaviruses begins with the attachment of the virus to the host cell via the spike protein. The virus then enters the cell, where its RNA genome is released and translated into viral proteins. The replication-transcription complex is formed, facilitating the synthesis of new viral RNA.
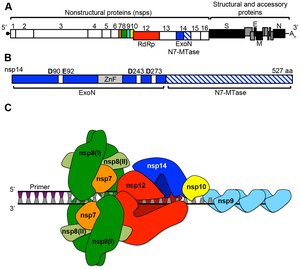
The newly synthesized viral RNA and proteins are assembled into virions, which are then released from the host cell to infect new cells.
Epidemiology[edit]
SARS-related coronaviruses have caused significant outbreaks, including the SARS outbreak in 2002-2003 and the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. These viruses have a high potential for human-to-human transmission, leading to widespread infection and significant public health challenges.
Prevention and Control[edit]
Preventive measures for SARS-related coronaviruses include vaccination, wearing masks, maintaining social distance, and practicing good hygiene. Vaccines have been developed for SARS-CoV-2, which have been instrumental in controlling the spread of COVID-19.
Related pages[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian