Ptaquiloside


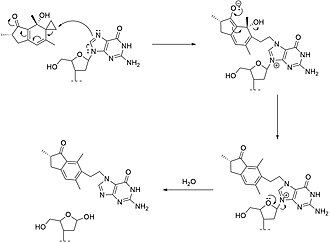


Ptaquiloside is a naturally occurring carcinogen found in certain species of fern, most notably in the bracken fern (Pteridium aquilinum). It is a norsesquiterpene glycoside, a type of chemical compound that has been linked to increased risks of cancer in animals and possibly humans. The presence of ptaquiloside in bracken ferns has implications for wildlife, livestock, and human health, as the consumption of bracken ferns can lead to poisoning and the development of cancers, particularly in the digestive tract.
Chemical Structure and Properties[edit]
Ptaquiloside has a complex chemical structure that includes a sugar molecule attached to a sesquiterpene, a class of terpenes consisting of three isoprene units. This structure is responsible for its toxic and carcinogenic properties. When ingested, ptaquiloside is metabolized into compounds that can bind to DNA, leading to mutations and cancer.
Occurrence[edit]
Ptaquiloside is found predominantly in the bracken fern, which grows widely around the world in various habitats. The concentration of ptaquiloside can vary significantly depending on the geographic location, time of year, and part of the plant, with higher concentrations typically found in the young fronds.
Health Implications[edit]
The health risks associated with ptaquiloside are a concern for both animals and humans. In livestock, consumption of bracken fern can lead to a condition known as bracken fern poisoning, characterized by acute or chronic disease states, including hemorrhagic disease and bladder and intestinal cancers. In humans, there is evidence to suggest that prolonged exposure to ptaquiloside, through the consumption of contaminated milk or meat from animals that have grazed on bracken, may increase the risk of certain cancers.
Environmental Impact[edit]
Ptaquiloside is also an environmental concern because it can leach into the soil and contaminate water sources, posing a risk to wildlife and potentially entering the human food chain. The stability of ptaquiloside in the environment and its ability to be absorbed by plants raise questions about the broader ecological impacts of bracken fern proliferation.
Management and Mitigation[edit]
Efforts to manage the risks associated with ptaquiloside include controlling the spread of bracken ferns, especially in areas used for grazing, and monitoring the health of livestock that may be exposed to the plant. Public health initiatives may also focus on raising awareness of the risks associated with consuming products derived from animals that have grazed on bracken.
Research Directions[edit]
Research into ptaquiloside continues to explore its mechanism of action, environmental fate, and potential strategies for mitigating its harmful effects. Understanding the pathways through which ptaquiloside causes cancer is crucial for developing preventive measures and treatments for those affected by exposure.
| This article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by registering to expand it. |
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian