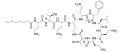
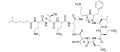
Polymyxin B
Polymyxin B is an antibiotic that belongs to the polymyxin group, which is known for its effectiveness against Gram-negative bacteria. It is a last-resort antibiotic used to treat serious infections caused by bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics. Polymyxin B works by binding to the lipopolysaccharides on the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria, disrupting the cell membrane and leading to cell death. This antibiotic is particularly used in treating infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, and Klebsiella pneumoniae, among others.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Polymyxin B exerts its bactericidal effects by interacting with the phospholipids and lipopolysaccharides in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. This interaction disrupts the integrity of the cell membrane, increasing its permeability, which leads to leakage of cellular contents and ultimately cell death. The specificity of polymyxin B for Gram-negative bacteria is due to its affinity for the lipopolysaccharides present in their outer membrane, which are absent in Gram-positive bacteria.
Clinical Uses[edit]
Polymyxin B is primarily used in the treatment of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections, including those caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, and Klebsiella pneumoniae. It is often reserved for cases where other treatments have failed due to its potential for nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity. Polymyxin B is administered intravenously or as a topical formulation for skin infections. It is also used in combination with other antibiotics to broaden its antibacterial spectrum and reduce the risk of resistance development.
Side Effects[edit]
The use of polymyxin B can be associated with several adverse effects, the most significant of which are nephrotoxicity (kidney damage) and neurotoxicity (damage to the nervous system). Other potential side effects include skin irritation when applied topically, and, less commonly, allergic reactions. Due to these risks, the use of polymyxin B is typically limited to situations where the benefits outweigh the potential harms, and it is administered under close medical supervision.
Resistance[edit]
The emergence of bacterial resistance to polymyxin B is a growing concern, particularly in the context of multidrug-resistant bacterial infections. Resistance mechanisms include modifications to the lipopolysaccharides in the bacterial outer membrane, which reduce the binding affinity of polymyxin B, thereby decreasing its effectiveness. The development of resistance underscores the need for judicious use of this antibiotic and the ongoing search for new antimicrobial agents.
Conclusion[edit]
Polymyxin B remains an important tool in the fight against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections. Its use, however, is tempered by its potential for serious side effects and the emergence of resistance. Ongoing research into its mechanisms of action, potential for toxicity, and strategies to mitigate resistance is essential to optimizing its clinical utility.
-
Polymyxin B1
-
Polymyxin B2
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian