Phosphorylase kinase
Phosphorylase kinase (PhK) is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the regulation of glycogen metabolism. It activates glycogen phosphorylase, the enzyme responsible for glycogen breakdown, through phosphorylation. This process is essential for the mobilization of glucose from glycogen stores, a critical function in both muscle and liver cells in response to physiological demands.
Structure[edit]
Phosphorylase kinase is a multimeric enzyme, consisting of four different subunits: alpha (α), beta (β), gamma (γ), and delta (δ), with the stoichiometry of (αβγδ)₄. The γ subunit is the catalytic core, possessing the enzyme's kinase activity. The δ subunit is actually the calmodulin protein, which binds calcium ions and is essential for the enzyme's activity. The α and β subunits are regulatory and undergo phosphorylation by various kinases, including protein kinase A, which modulates the activity of PhK.
Function[edit]
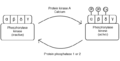
The primary function of phosphorylase kinase is to phosphorylate and thereby activate glycogen phosphorylase, the enzyme that catalyzes the first step in glycogen breakdown. This activation is part of the glycogenolysis pathway, which mobilizes glucose units from glycogen stores for energy production. PhK itself is activated through a cascade of events triggered by hormonal signals like adrenaline and glucagon or by an increase in intracellular calcium levels, which can occur during muscle contraction.
Regulation[edit]
The activity of phosphorylase kinase is regulated by multiple mechanisms:
- Phosphorylation: PhK is activated by phosphorylation of its α and β subunits, a reaction catalyzed by protein kinase A. This modification enhances the enzyme's activity.
- Calcium binding: The binding of calcium ions to the δ subunit (calmodulin) induces a conformational change in PhK, increasing its activity. This mechanism links PhK activation to intracellular calcium levels, making it responsive to muscle contraction and other signals that elevate calcium.
- Allosteric regulation: PhK activity can also be modulated by allosteric effectors, including ATP and glucose-6-phosphate, which can fine-tune the enzyme's activity in response to the energy status of the cell.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Mutations in the genes encoding the subunits of phosphorylase kinase can lead to a rare condition known as Glycogen Storage Disease IX (GSD IX), characterized by an accumulation of glycogen in tissues, particularly the liver and muscles. This condition can result in hepatomegaly, growth retardation, hypoglycemia, and, in some cases, muscle weakness.
Research Directions[edit]
Research on phosphorylase kinase continues to explore its structure-function relationships, regulatory mechanisms, and its role in various physiological and pathological processes. Understanding the intricate regulation of PhK could lead to new therapeutic strategies for treating metabolic disorders, including glycogen storage diseases and diabetes.

This article is a biochemistry stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian