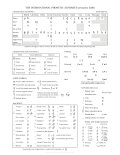
Phonetic transcription
Phonetic transcription is a system used to visually represent the sounds of speech. Unlike the standard writing systems of most languages, which focus on representing the meaning of words, phonetic transcription specifically aims to accurately depict how words are pronounced. This is crucial in linguistics, language teaching, and lexicography, as it provides a standardized method to record and analyze the myriad sounds in human speech. The most widely used system of phonetic transcription is the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), which offers a unique symbol for each sound found in human spoken language.
Overview[edit]
Phonetic transcription serves several key functions. It helps linguists document languages, including those that are not written or are poorly documented. It is also an essential tool in the study of phonology and phonetics, the branches of linguistics concerned with the sounds of languages. In language teaching, phonetic transcription provides learners with a way to understand pronunciation nuances that may not be obvious from the spelling of words.
Types of Phonetic Transcription[edit]
There are two main types of phonetic transcription: broad and narrow. Broad transcription, also known as phonemic transcription, uses a simple set of symbols to represent the phonemes or distinct sounds of a language, without detailing every possible phonetic variation. Narrow transcription, or allophonic transcription, uses a more complex set of symbols and diacritics to capture the exact pronunciation of words, including regional accents and individual speaker variations.
The International Phonetic Alphabet[edit]
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is the most comprehensive and widely adopted system for phonetic transcription. Developed by the International Phonetic Association, the IPA provides a set of symbols that correspond to the sounds used in spoken languages around the world. The alphabet is divided into categories such as consonants, vowels, suprasegmentals (which include intonation and stress), and diacritics, which modify the pronunciation of other symbols.
Applications of Phonetic Transcription[edit]
Phonetic transcription has a wide range of applications. In linguistics, it is used for phonetic and phonological analysis, helping researchers understand the structure and function of sounds in languages. In language education, teachers use phonetic transcription to show students the pronunciation of words, especially in languages with irregular spelling systems. In speech therapy and audiology, phonetic transcription helps professionals diagnose and treat speech and hearing disorders. Additionally, actors and singers often use phonetic transcription to learn accents or pronunciations for performances.
Challenges and Limitations[edit]
Despite its utility, phonetic transcription is not without challenges. The precision of narrow transcription requires extensive training and can be time-consuming. Moreover, the IPA does not account for all the nuances of speech, such as tone of voice or emotional inflection. There is also the issue of variability among speakers, including differences in accent, dialect, and individual speech patterns, which can make consistent transcription difficult.
Conclusion[edit]
Phonetic transcription is a vital tool in the study and teaching of languages, offering a precise method for representing the sounds of speech. The International Phonetic Alphabet, as the standard system of phonetic transcription, plays a crucial role in linguistics, language education, and related fields. Despite its challenges, phonetic transcription remains an essential technique for understanding the phonetic and phonological aspects of human language.

This article is a linguistics stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
International Phonetic Alphabet chart 2020
-
Visible Speech illustrations
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian