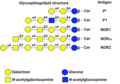
P1PK blood group system
P1PK blood group system, also known as the Globoside blood group system, encompasses a collection of antigens found on the surface of red blood cells and other tissues. These antigens are significant in the field of transfusion medicine and have implications in certain medical conditions, including hemolytic disease of the newborn. The system is defined by the presence or absence of specific glycolipid substances in the cell membrane, which are recognized by corresponding antibodies. The most notable antigens in this system are P1, Pk, and NOR.
Antigens and Genetics[edit]
The P1PK blood group system is determined by the A4GALT gene, which encodes the enzyme alpha 1,4-galactosyltransferase. This enzyme is responsible for the synthesis of the Pk antigen (Gb3), which is a precursor for the P antigen (Gb4). The presence of the P1 antigen is dependent on the activity of another enzyme, which adds an additional sugar molecule to the P antigen. The genetic basis of these antigens explains the variability in their expression among different individuals.
Clinical Significance[edit]
The clinical relevance of the P1PK blood group system is primarily observed in transfusion medicine and in cases of hemolytic disease of the newborn. Antibodies against these antigens can arise in individuals who lack them, potentially leading to transfusion reactions if blood containing the antigen is transfused. Similarly, if a pregnant woman lacks a specific antigen that is present in the fetus, she may develop antibodies against the fetal red blood cells, leading to hemolytic disease of the newborn.
Transfusion Reactions[edit]
Transfusion reactions related to the P1PK blood group system are rare but can occur when blood from a donor with a different P1PK phenotype is transfused into a recipient with antibodies against one or more of the antigens in this system. These reactions can range from mild to severe and underscore the importance of thorough blood typing and crossmatching in transfusion practices.
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn[edit]
Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) due to antibodies against the P1PK antigens is uncommon. However, when it does occur, it can result in varying degrees of anemia, jaundice, and in severe cases, hydrops fetalis. Management of HDN involves close monitoring and, in some cases, intervention such as phototherapy or exchange transfusion.
Blood Typing and Identification[edit]
Identification of the P1PK antigens is performed through serological testing, using specific anti-P1, anti-Pk, and anti-NOR antibodies. These tests are essential for safe blood transfusion practices and for the investigation of hemolytic disease of the newborn related to the P1PK blood group system.
See Also[edit]
P1PK_blood_group_system[edit]
-
P1PK antigen structures
-
Serology interpretation of antibody panel for blood group antigens
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian