Occupational hearing loss
Occupational hearing loss refers to the impairment of hearing resulting from exposure to hazardous noise or ototoxic chemicals in the workplace. This condition is a significant global health concern, affecting millions of workers across various industries, including manufacturing, construction, military, and music. Occupational hearing loss can range from temporary changes in hearing to permanent damage, including tinnitus and sensorineural hearing loss.
Causes[edit]
The primary cause of occupational hearing loss is prolonged exposure to high levels of noise, typically above 85 decibels (dB) over an 8-hour workday, as recommended by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Ototoxic substances, which are chemicals that damage the inner ear or the vestibulo-cochlear nerve, also contribute to occupational hearing loss. These substances include certain solvents, metals, and asphyxiants that are present in various industrial settings.
Prevention[edit]
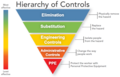
Preventing occupational hearing loss involves a combination of engineering controls, administrative controls, and personal protective equipment (PPE). Engineering controls aim to reduce noise at the source through modifications to equipment and processes. Administrative controls include implementing policies to limit the duration and intensity of noise exposure. Personal protective equipment, such as earplugs and earmuffs, provides a barrier between the noise and the individual's ears.
Screening and Diagnosis[edit]
Regular hearing tests, known as audiometric evaluations, are crucial for early detection of occupational hearing loss. These tests help in identifying individuals at risk and in implementing timely interventions. Diagnosis typically involves a thorough history taking, physical examination, and audiometric testing to assess the type and degree of hearing loss.
Management and Treatment[edit]
Management of occupational hearing loss focuses on preventing further damage and improving quality of life for affected individuals. This may include the use of hearing aids, assistive listening devices, and, in some cases, cochlear implants. Education and training on safe listening practices are also essential components of managing occupational hearing loss.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects[edit]
Various countries have established regulations and guidelines to protect workers from occupational noise exposure. In the United States, OSHA sets enforceable standards that require employers to implement hearing conservation programs when noise levels exceed 85 dB. Similar regulations exist in other countries, aiming to reduce the incidence of occupational hearing loss.
Conclusion[edit]
Occupational hearing loss is a preventable condition that poses significant challenges to workers' health and productivity. Through comprehensive prevention strategies, early detection, and effective management, it is possible to mitigate the impact of hazardous noise and ototoxic chemicals in the workplace.
-
Prevalence of Hearing Loss by Time Period and Industry Sector, 1981 - 2010 for 1,816,812 workers
-
NIOSH Sound Level Meter
-
NIOSH Hierarchy of Controls
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian