Nipple shield (breastfeeding)
Nipple shield (breastfeeding) is a breastfeeding accessory used to help facilitate the nursing process. A nipple shield is typically made of thin, flexible silicone and is worn over the nipple and areola during breastfeeding. Its primary purposes are to protect sore or cracked nipples, to help babies latch on to the breast more easily, and to assist in breastfeeding babies with special challenges such as prematurity or cleft palate.
Usage[edit]
Nipple shields are often recommended by lactation consultants or healthcare providers in specific situations where breastfeeding is difficult or painful. These situations may include issues with latch-on, engorgement, flat or inverted nipples, or when a baby is transitioning from bottle-feeding back to breastfeeding. However, it is important to use nipple shields under the guidance of a breastfeeding specialist, as improper use can lead to reduced milk supply or nipple confusion for the baby.
Types[edit]
There are several types of nipple shields available, varying in size, shape, and thickness. The most common type is the contact nipple shield, which has a cut-out section to allow more skin-to-skin contact between the mother and baby during breastfeeding. Choosing the right type and size of nipple shield is crucial for its effectiveness and to prevent further complications.
Benefits and Risks[edit]
Benefits[edit]
- Helps babies with latch-on difficulties to breastfeed effectively.
- Protects sore or cracked nipples during breastfeeding, allowing them to heal.
- Assists in breastfeeding premature babies or those with special needs, such as cleft palate.
Risks[edit]
- Potential for reduced milk transfer to the baby, which can affect weight gain.
- Risk of nipple confusion, where the baby prefers the shield over the natural nipple.
- Possible dependency on the shield, making it difficult to transition away from its use.
Guidelines for Use[edit]
To minimize the risks and maximize the benefits of using a nipple shield, the following guidelines are recommended:
- Consult with a lactation consultant or healthcare provider before starting to use a nipple shield.
- Ensure the nipple shield is the correct size and shape for your nipple.
- Use the nipple shield for the shortest time possible, and try to wean off it under professional guidance.
- Monitor the baby's weight and milk intake to ensure they are receiving enough breast milk.
Cleaning and Maintenance[edit]
Proper cleaning and maintenance of the nipple shield are essential to prevent infections. After each use, the nipple shield should be washed with warm soapy water, rinsed thoroughly, and allowed to air dry. Sterilization methods recommended by the manufacturer can be followed for additional safety.
Conclusion[edit]
While nipple shields can be a helpful tool for some breastfeeding challenges, they should be used with caution and under professional guidance. It is important to address the underlying issues causing breastfeeding difficulties with the help of a lactation consultant or healthcare provider.
-
Nipple shield (breastfeeding)
-
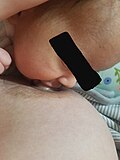
Silicone nipple shield after application
-
Silicone nipple shield before application
-
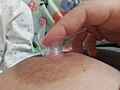
Placing a nipple shield
-
Nipple shield in place
-
Nipple shield (breastfeeding)
-
Sterling silver, ivory and glass nipple shield
-
Glass nipple shield, 1851-1900
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian