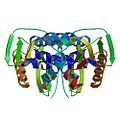
NS1 influenza protein
NS1 influenza protein is a non-structural protein encoded by the influenza virus. It plays a crucial role in the virus's ability to infect its host and evade the host's immune system. The NS1 protein is involved in multiple stages of the viral life cycle, including replication, inhibition of host antiviral response, and modulation of the host cell environment to favor viral replication.
Function[edit]
The primary function of the NS1 protein is to counteract the host's antiviral defenses. It achieves this by inhibiting the production of interferons, proteins that are crucial for the antiviral response. NS1 interferes with the interferon production pathway by binding to and sequestering key molecules required for the activation of the interferon genes. Additionally, NS1 can bind to double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), preventing the activation of RNA-activated protein kinase (PKR), which is another important component of the host's antiviral response.
NS1 also interacts with other host cellular machinery to enhance viral replication. For example, it can bind to specific host ribonucleoproteins to stabilize viral mRNAs, ensuring efficient translation of viral proteins. Furthermore, NS1 has been shown to modulate the host cell's apoptosis pathways, delaying cell death and providing the virus with more time to replicate and spread.
Structure[edit]
The NS1 protein varies in length among different influenza strains, typically ranging from 230 to 237 amino acids. Its structure is divided into two main domains: an N-terminal RNA-binding domain and a C-terminal effector domain. The RNA-binding domain allows NS1 to bind dsRNA molecules, while the effector domain interacts with various host proteins to inhibit the interferon response and modulate other cellular processes.
Variability and Evolution[edit]
The NS1 protein exhibits a high degree of variability among different influenza virus strains. This variability is a result of the virus's rapid mutation rate and the selective pressure exerted by the host's immune system. Changes in the NS1 protein can affect the virus's virulence and its ability to evade the host's immune response. As such, studying the evolution and variability of the NS1 protein is crucial for understanding influenza pathogenesis and for the development of effective vaccines and antiviral drugs.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Given its critical role in viral pathogenesis, the NS1 protein is a target for antiviral drug development. Inhibitors that can block the function of NS1 have the potential to enhance the host's antiviral response and reduce the severity of influenza infection. Additionally, variations in the NS1 protein among different influenza strains can influence the effectiveness of vaccines. Understanding the mechanisms by which NS1 evades the immune response can inform the design of more effective vaccines and therapeutic strategies.
-
NS1 Dimer Influenza H5N1
-
The Acid Elution Principle
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian