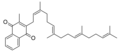
Menatetrenone
Menatetrenone, also known as vitamin K2 or MK-4, is a type of Vitamin K that is involved in the modification of certain proteins, making them able to bind calcium ions. This process is essential for the proper functioning of the body, including bone formation and blood coagulation. Menatetrenone is synthesized by animal tissues and is also found in certain fermented foods.
Sources[edit]
Menatetrenone is primarily found in animal-based foods, such as meat, eggs, and dairy products. It is also present in high amounts in certain fermented foods, particularly Nattō, a traditional Japanese food made from fermented soybeans. Unlike its counterpart, Vitamin K1 (phylloquinone), which is found in green leafy vegetables, menatetrenone is not as widely available in the diet.
Biochemistry[edit]
Menatetrenone works by activating proteins that are involved in calcium metabolism. The most notable of these proteins are Osteocalcin, which is involved in bone formation, and Matrix Gla Protein (MGP), which inhibits calcification of arteries and cartilage. Menatetrenone achieves this by carboxylating specific glutamate residues on these proteins, a process that allows them to bind calcium ions.
Health Benefits[edit]
- Bone Health ###
Menatetrenone has been shown to play a significant role in maintaining bone health. It increases bone mineral density and reduces the risk of fractures, particularly in individuals with Osteoporosis. Its role in activating osteocalcin is particularly important for the incorporation of calcium into the bone matrix.
- Cardiovascular Health ###
By activating MGP, menatetrenone helps prevent the calcification of blood vessels and, therefore, may contribute to cardiovascular health. It has been suggested that higher intakes of vitamin K2 could be associated with a reduced risk of Coronary Heart Disease.
Clinical Use[edit]
Menatetrenone has been used in the treatment of osteoporosis in Japan. It is often prescribed alongside calcium and vitamin D supplements to enhance bone health and prevent fractures. There is also ongoing research into its potential benefits in preventing and treating other conditions, such as cardiovascular diseases and certain cancers.
Side Effects and Interactions[edit]
Menatetrenone is generally considered safe when consumed in amounts found in foods or as part of a balanced diet. However, when taken in high doses as a supplement, it may interact with anticoagulant medications, such as Warfarin, by antagonizing their effect. Patients on anticoagulant therapy should consult with a healthcare provider before taking menatetrenone supplements.
Conclusion[edit]
Menatetrenone is an important nutrient that plays a crucial role in bone and cardiovascular health. While it is not as widely recognized as other vitamins, its benefits in preventing and treating osteoporosis and potentially reducing the risk of coronary heart disease make it an important area of research and clinical interest.
This vitamin-related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
Menatetrenone[edit]
-
Menatetrenone
-
Menatetrenone molecule spacefill
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian