MRNA vaccine
mRNA Vaccine[edit]
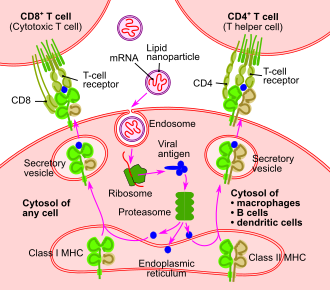
An mRNA vaccine is a type of vaccine that uses a copy of a molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA) to produce an immune response. The mRNA in the vaccine encodes a protein that is part of the pathogen, such as a virus, which the immune system learns to recognize and combat. This innovative approach to vaccination has been pivotal in the rapid development of vaccines against COVID-19.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
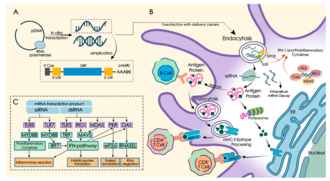
mRNA vaccines work by introducing a synthetic mRNA sequence into the body. This mRNA sequence is encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles to protect it from degradation and facilitate its entry into cells. Once inside the cells, the mRNA is translated by the cell's ribosomes into the target protein, typically a viral antigen.
The immune system recognizes this protein as foreign, triggering an immune response. This response includes the activation of T cells and the production of antibodies by B cells. The immune system "remembers" the protein, allowing it to mount a faster and more effective response if it encounters the actual virus in the future.
Development and Use[edit]
File:MRNA vaccines against the coronavirus.webm
The development of mRNA vaccines has been accelerated by advances in genetic engineering and nanotechnology. The first mRNA vaccines to be authorized for emergency use were the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine and the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine. These vaccines have shown high efficacy in preventing COVID-19 and have been distributed globally.
mRNA vaccines offer several advantages over traditional vaccines. They can be developed rapidly, as they do not require the growth of pathogens in the laboratory. Additionally, mRNA vaccines can be easily modified to target new variants of a virus, making them adaptable to emerging infectious diseases.
Safety and Efficacy[edit]

Clinical trials have demonstrated that mRNA vaccines are both safe and effective. Common side effects include mild to moderate symptoms such as fever, fatigue, and muscle pain, which are typical of many vaccines. Serious adverse events are rare.
The efficacy of mRNA vaccines in preventing symptomatic COVID-19 has been reported to be over 90% in clinical trials. Ongoing studies continue to monitor the long-term safety and effectiveness of these vaccines.
Challenges and Future Directions[edit]

Despite their success, mRNA vaccines face challenges, particularly in distribution and storage. They require cold chain logistics, as they must be stored at low temperatures to maintain stability. Efforts are underway to develop formulations that are stable at higher temperatures.
Future research is focused on expanding the use of mRNA technology to other infectious diseases and even cancer vaccines. The flexibility and rapid development potential of mRNA vaccines make them a promising tool in the fight against global health threats.
Related Pages[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian