Lycium barbarum

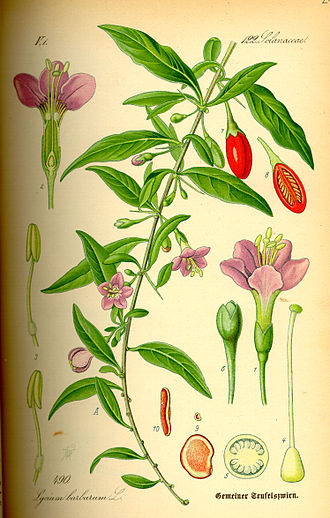

Lycium barbarum is a species of boxthorn in the family Solanaceae that is native to certain regions of Asia and Europe. It is commonly known as goji berry, wolfberry, and red medlar. This plant plays a significant role in traditional Chinese medicine and has been cultivated for its nutritional and medicinal properties for centuries. The berries of Lycium barbarum are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, making them a popular ingredient in various health supplements and foods.
Description[edit]
Lycium barbarum is a deciduous woody perennial plant, growing 1 to 3 meters in height. It has lanceolate leaves that are 7–14 cm long and 3.5–5 cm broad. The flowers are small, purple, or lavender, with a bell-shaped corolla. The fruit is an orange-red berry 1–2 cm in diameter. The berries are often dried and eaten as a snack, brewed in teas, or used in medicinal concoctions.
Distribution and Habitat[edit]
Originally from southeastern Europe and Asia, Lycium barbarum has been introduced to other continents, including North America and Australia, where it is grown both as an ornamental plant and for its berries. It thrives in well-drained, alkaline soils and requires full sun for optimal growth and fruit production.
Cultivation[edit]
Cultivation of Lycium barbarum requires careful management of watering and sunlight exposure. The plants are drought-tolerant but produce higher yields with regular irrigation. They are also relatively resistant to pests and diseases, making them suitable for organic farming practices. Pruning is essential to maintain plant health and maximize berry production.
Nutritional and Medicinal Properties[edit]
The berries of Lycium barbarum are highly nutritious, containing a rich blend of vitamins A and C, iron, selenium, and other antioxidants such as zeaxanthin. They are reputed to have multiple health benefits, including boosting the immune system, protecting against heart disease, and improving vision. In traditional Chinese medicine, goji berries are used to treat kidney and liver problems, promote longevity, and improve sexual function.
Culinary Uses[edit]
Goji berries are versatile in culinary applications. They can be eaten raw, dried, or cooked. They are often added to soups, porridge, and teas in Chinese cuisine. In Western countries, goji berries are commonly found in health food products like smoothies, bars, and supplements.
Controversies and Research[edit]
While Lycium barbarum and its berries are touted for their health benefits, scientific research supporting these claims is mixed. Some studies suggest potential health benefits, while others indicate that more research is needed to substantiate the claims made about goji berries' nutritional and medicinal properties.
Conservation Status[edit]
Lycium barbarum is not currently listed as endangered or threatened. However, its habitat and wild populations could be affected by overharvesting and land use changes. Sustainable cultivation practices are essential to ensure the long-term availability of this valuable plant.
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
