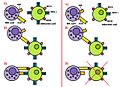
Killer activation receptor
Killer Activation Receptor (KAR) is a type of receptor found on the surface of certain immune cells, notably Natural Killer (NK) cells. These receptors play a crucial role in the immune system's ability to recognize and destroy infected or malignant cells. Understanding the function and mechanisms of KARs is essential for advancing immunotherapy and developing treatments for cancer and viral infections.
Overview[edit]
Killer Activation Receptors are part of a larger family of receptors known as NK cell receptors. NK cells are a type of lymphocyte, or white blood cell, that plays a vital role in the innate immune response. Unlike T cells and B cells of the adaptive immune system, NK cells do not require prior exposure to a pathogen to recognize and attack it. Instead, they rely on a balance of activating and inhibitory signals received through their receptors to determine whether to kill a target cell.
Function[edit]
The primary function of KARs is to recognize specific ligands (molecules) expressed on the surface of stressed, transformed, or infected cells. When a KAR binds to its ligand, it sends an activating signal to the NK cell, prompting it to release cytotoxic granules that can kill the target cell. This mechanism is crucial for the early defense against viral infections and for the surveillance against cancerous cells.
Types of KARs[edit]
There are several types of Killer Activation Receptors, each with its specific ligands and signaling pathways. Some well-known KARs include:
- NKG2D: Recognizes stress-induced ligands often upregulated in infected or tumor cells.
- NKp46, NKp30, and NKp44: Part of the natural cytotoxicity receptors (NCRs) that play a key role in the recognition and killing of tumor cells.
Regulation[edit]
The activity of KARs is tightly regulated to prevent unintended tissue damage. NK cells must integrate signals from both activating receptors like KARs and inhibitory receptors to make a decision. Inhibitory receptors recognize molecules such as MHC class I presented on healthy cells, providing a "don't kill" signal that counterbalances the activating signals.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Understanding the pathways and mechanisms of KARs has significant implications for clinical medicine. Therapeutic strategies that enhance the activation of NK cells through KARs are being explored for cancer immunotherapy. Additionally, some viral pathogens have evolved mechanisms to evade NK cell detection by downregulating ligands for KARs, highlighting the importance of these receptors in antiviral defense.
Research and Future Directions[edit]
Research into Killer Activation Receptors continues to uncover new ligands, signaling pathways, and regulatory mechanisms. Future therapies may involve manipulating KARs or their ligands to boost the immune response against cancer or to create more effective vaccines against viral infections.

This article is a immunology stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!

This article is a cell biology stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
KAR image
-
KAR fosforilation
Killer_activation_receptor[edit]
-
Killer activation receptor image
-
Killer activation receptor phosphorylation
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian