Focused ultrasound
Focused Ultrasound is a therapeutic technology that uses ultrasound to target tissue deep in the body without incisions or radiation. It is an early-stage, non-invasive, therapeutic technology with the potential to improve the quality of life and decrease the cost of care for patients with a variety of medical conditions.
History[edit]
The concept of focused ultrasound was first proposed in the 1940s, but it was not until the late 20th century that significant advancements were made in the field. The development of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in the 1970s and 1980s provided a means to monitor and control the treatment in real time, leading to the first FDA approval of a focused ultrasound device in 2004.
Technology[edit]
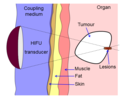
Focused ultrasound works by focusing multiple intersecting beams of ultrasound on a target. Each individual beam passes through tissue with little effect but at the focal point where the beams converge, the energy can have useful thermal or mechanical effects. This technology can be used to destroy tissue, such as tumors, or to stimulate the body's response to disease.
Applications[edit]
Focused ultrasound is currently approved in the United States for the treatment of uterine fibroids and bone metastases. It is also being investigated for the treatment of a variety of other conditions, including Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and essential tremor.
Future[edit]
The future of focused ultrasound is promising, with ongoing research exploring new applications and improving the technology. The Focused Ultrasound Foundation, a global nonprofit dedicated to accelerating the development and adoption of focused ultrasound, is leading efforts to advance this field.
See also[edit]
- Ultrasound
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Uterine fibroids
- Bone metastases
- Parkinson's disease
- Alzheimer's disease
- Essential tremor
This radiology related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
Focused_ultrasound[edit]
-
Diagram showing liver lesioning using a HIFU transducer
-
MRI-guided HIFU for essential tremor
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian