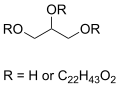
Glyceryl behenate

Glyceryl behenate is a lipid compound, specifically an ester of behenic acid and glycerol. It is commonly used in the pharmaceutical and cosmetics industries as an excipient and a thickening agent, respectively. Glyceryl behenate is known for its high melting point and is utilized in various formulations to improve the texture and stability of products.
Properties[edit]
Glyceryl behenate is characterized by its long-chain fatty acid, which contributes to its high melting point, making it solid at room temperature. This property is particularly beneficial in the formulation of solid dosage forms in the pharmaceutical industry, such as tablets and capsules, as it aids in controlling the release of the active pharmaceutical ingredient. In cosmetics, its ability to solidify and stabilize formulations makes it an ideal ingredient in lipsticks, deodorants, and skin creams.
Applications[edit]
Pharmaceutical[edit]
In the pharmaceutical industry, glyceryl behenate is used as a lubricant, binder, and disintegrant in the manufacturing of tablets and capsules. Its lubricating properties help in the easy compression of tablets and reduce wear on the machinery during the tablet production process. As a binder, it assists in holding the ingredients of a tablet together, while as a disintegrant, it helps in the tablet's dissolution, ensuring that the active ingredients are released appropriately.
Cosmetics[edit]
In cosmetics, glyceryl behenate is valued for its ability to improve the texture and stability of products. It acts as a thickening agent in creams and lotions, providing a desirable consistency. Additionally, it is used in lipsticks for its solidifying properties, which help in achieving the right hardness and texture, making the application smoother.
Regulatory Status[edit]
Glyceryl behenate is recognized as safe for use in both pharmaceutical and cosmetic products. Regulatory bodies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe, have approved its use within specified limits. It is important for manufacturers to adhere to these regulations to ensure the safety and efficacy of their products.
Conclusion[edit]
Glyceryl behenate plays a crucial role in the formulation of various pharmaceutical and cosmetic products. Its unique properties, such as high melting point and ability to act as a lubricant, binder, and thickening agent, make it a valuable ingredient in improving the texture, stability, and release of active ingredients in these products. As with any excipient, its use is governed by regulatory authorities to ensure product safety and efficacy.
-
Glyceryl behenate
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian