Functional magnetic resonance imaging
| Functional magnetic resonance imaging | |
|---|---|
| [[File:|250px|alt=|]] | |
| Pronunciation | |
| Synonyms | |
| Reference Range | |
| Calculator | |
| Purpose | |
| Test of | |
| Based on | |
| ICD-10-PCS | |
| ICD-9-CM | |
| MeSH | |
| OPS-301 Code | |
| Other Codes | |
| MedlinePlus | |
| eMedicine | |
| LOINC | |
| HCPCS-L2 | |
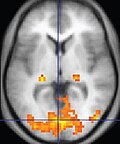
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) is a neuroimaging procedure that measures and maps the brain's activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area of the brain is in use, blood flow to that region also increases. The primary form of fMRI uses the blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) contrast, which is sensitive to changes in the oxygenation of blood.
History[edit]
The development of fMRI in the 1990s was a significant breakthrough in the field of neuroscience. It evolved from earlier MRI scanning technology, incorporating the understanding that blood flow and neuronal activity are linked.
Principles[edit]
fMRI works by detecting the changes in blood oxygenation and flow that occur in response to neural activity. When a brain area is more active, it consumes more oxygen, and to meet this increased demand, blood flow increases to the active area. fMRI can thus capture images of the changing blood flow related to energy use by brain cells.
Applications[edit]
fMRI is used in both research and clinical settings:
- In research, fMRI is used to assess brain function, supporting studies on brain mapping and the understanding of various neurological and psychological phenomena.
- Clinically, fMRI helps surgeons plan surgeries in critical brain areas, aids in the assessment of brain damage, and is used in the diagnosis of disorders like Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia.
Procedure[edit]
During an fMRI scan, the patient lies on a table that slides into a large tunnel-shaped scanner. They must remain still during the scan. Typically, the scan sequences are synchronized with tasks that the subject performs, which can involve answering questions, looking at images, or listening to sounds.
Advantages and Limitations[edit]
Advantages[edit]
- Non-invasive and does not involve radiation, making it safe for repeated use.
- Provides both anatomical and functional information, making it invaluable for research and clinical purposes.
Limitations[edit]
- Expensive and requires specialized equipment and personnel.
- The presence of metal in the body can be a contraindication.
- Limited temporal resolution compared to other methods like electroencephalography (EEG).
Future Directions[edit]
Ongoing research in fMRI technology aims to improve the spatial and temporal resolution of the scans. Advances in machine learning and data analysis are also enhancing the interpretation of fMRI data, leading to more precise brain mapping.
-
Functional magnetic resonance imaging
-
Functional magnetic resonance imaging
-
Functional magnetic resonance imaging
-
Functional magnetic resonance imaging
-
Functional magnetic resonance imaging
-
Functional magnetic resonance imaging
-
Functional magnetic resonance imaging
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian