Expectation–maximization algorithm
Expectation–maximization (EM) algorithm is a powerful statistical method used for finding maximum likelihood estimates of parameters in probabilistic models, where the model depends on unobserved latent variables. The EM algorithm is an iterative method that alternates between performing an expectation (E) step, which creates a function for the expectation of the log-likelihood evaluated using the current estimate for the parameters, and a maximization (M) step, which computes parameters maximizing the expected log-likelihood found on the E step. These steps are repeated until convergence.
Overview[edit]
The EM algorithm was introduced in a seminal paper by Arthur Dempster, Nan Laird, and Donald Rubin in 1977. It has since become a crucial tool in the field of statistics and machine learning for dealing with incomplete data sets or hidden variables, common in many applications such as speech recognition, computational biology, and image analysis.
Algorithm[edit]
The EM algorithm consists of two main steps repeated iteratively:
E-step[edit]
During the Expectation step, the algorithm calculates the expected value of the log-likelihood function, with respect to the conditional distribution of the latent variables given the observed data and the current estimates of the parameters. This step involves computing the expectation of the log-likelihood concerning the missing data, treating the parameters as fixed.
M-step[edit]
In the Maximization step, the parameters are updated to maximize the expected log-likelihood found in the E-step. This typically involves setting the derivative of the expected log-likelihood with respect to the parameters to zero and solving for the parameters.
Convergence[edit]
The EM algorithm is guaranteed to converge to a local maximum (or saddle point) of the likelihood function. Under certain conditions, it can be shown that the sequence of parameter estimates generated by the EM algorithm converges to the set of parameters that maximize the likelihood function.
Applications[edit]
The EM algorithm is widely used in various fields, including:
- Machine Learning: For clustering and density estimation in unsupervised learning.
- Bioinformatics: In the analysis of gene expression data and sequence alignment.
- Image Processing: For image reconstruction and segmentation.
- Speech Recognition: In hidden Markov models for recognizing speech patterns.
Limitations[edit]
While the EM algorithm is a powerful tool, it has some limitations:
- It can converge to a local maximum rather than the global maximum of the likelihood function.
- The convergence rate can be slow, especially in the presence of many local maxima.
- Choosing appropriate initial values for the parameters can significantly affect the algorithm's performance.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- Dempster, A. P., Laird, N. M., & Rubin, D. B. (1977). Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological).

This article is a algorithms or data structures-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
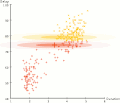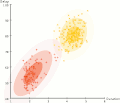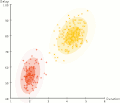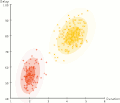
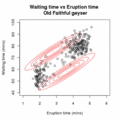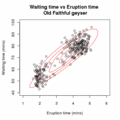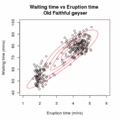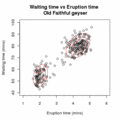
EM Clustering of Old Faithful data
-
Cluster Analysis Mouse
-
EM Old Faithful
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian