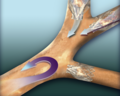
Endobronchial valve
Endobronchial valve (EBV) is a medical device used in the treatment of severe emphysema, a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The device is designed to improve lung function, reduce breathlessness, and enhance the quality of life for patients with emphysema by isolating the diseased portion of the lung, thereby reducing its volume and allowing the healthier parts of the lung to function more effectively.
Overview[edit]
Endobronchial valves are small, one-way valves that are placed inside the airways (bronchi) of the lung during a minimally invasive procedure called bronchoscopy. These valves allow air to exit the diseased part of the lung without letting air back in. This process is known as lung volume reduction. Over time, the treated portion of the lung collapses, making more room for the expansion of healthier lung tissue.
Indications[edit]
The primary indication for the use of endobronchial valves is for patients with severe emphysema who have not responded adequately to medical management, including medications and pulmonary rehabilitation. Candidates for this procedure typically have heterogeneous emphysema with areas of the lung that are more damaged than others and little to no collateral ventilation in the target lobe.
Procedure[edit]
The placement of endobronchial valves is performed during a bronchoscopy, which is a procedure that allows doctors to look inside the airways of the lungs using a thin, flexible tube called a bronchoscope. The procedure is usually done under sedation or general anesthesia. Using the bronchoscope, the physician navigates to the targeted area of the lung and places the valves in the airways leading to the diseased part of the lung.
Benefits[edit]
Patients who undergo this procedure may experience significant improvements in lung function, exercise capacity, and quality of life. The reduction in lung volume can lead to a decrease in breathlessness, making it easier for patients to perform daily activities.
Risks and Complications[edit]
As with any medical procedure, the placement of endobronchial valves carries certain risks. These may include pneumothorax (collapsed lung), exacerbation of COPD symptoms, pneumonia, and, in rare cases, death. However, for many patients, the potential benefits of the procedure outweigh the risks.
Conclusion[edit]
Endobronchial valves represent a significant advancement in the treatment of severe emphysema. By providing a minimally invasive option for lung volume reduction, they offer hope to patients who have limited treatment options. As with any medical intervention, careful patient selection and thorough discussion of the potential risks and benefits are essential.
-
Endobronchial valves placed in airways
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian