Electricity
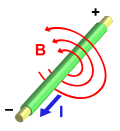
Electricity is a form of energy resulting from the existence of charged particles (such as electrons or protons), either statically as an accumulation of charge or dynamically as a current.
Overview[edit]
Electricity is a secondary energy source that we get from the conversion of other sources of energy, such as coal, natural gas, oil, nuclear power, and other natural sources. These are called primary sources. The energy sources we use to make electricity can be renewable or non-renewable, but electricity itself is neither renewable nor non-renewable.
History[edit]
The discovery of electricity is often linked to Benjamin Franklin's famous kite experiment in the 18th century, but electricity and its effects were observed long before this. Ancient Egyptians were aware of shocks from electric fish, and Greek philosophers noted that rubbing fur on various substances, like amber, would cause an attraction between the two.
Generation[edit]
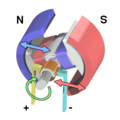
Electricity is most often generated at a power station by electromechanical generators, primarily driven by heat engines fueled by combustion or nuclear fission but also by other means such as the kinetic energy of flowing water and wind. Other energy sources include solar photovoltaics and geothermal power.
Distribution[edit]
Electricity is usually sold by the kilowatt hour (3.6 MJ) which is the product of the power in kilowatts multiplied by running time in hours. Electric utilities measure power using an electricity meter, which keeps a running total of the electric energy delivered to a customer.
Uses[edit]
Electricity is used for a vast number of purposes, including lighting, heating, cooling, and powering appliances and machines. It is also used in telecommunications, transportation, and in medical applications such as electrocardiograms and x-ray machines.
Safety[edit]
While electricity is incredibly useful, it is also potentially dangerous. Electrical shock can cause injury or death, and electrical fires can cause significant property damage. Therefore, it is important to follow safety guidelines when using electricity.
See also[edit]
- Electric power
- Electric energy consumption
- Electric field
- Electric charge
- Electric potential
- Electric current
References[edit]
<references />
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian