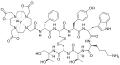
Edotreotide
Edotreotide is a synthetic compound used in the field of nuclear medicine for diagnostic purposes. It is a type of radiopharmaceutical that is specifically designed to target certain types of tumors, making it a valuable tool in the diagnosis and management of neuroendocrine tumors. Edotreotide, also known by its trade name as OctreoScan, is a somatostatin analog that mimics the natural somatostatin hormone in the body, which inhibits the growth of endocrine cells and the secretion of various hormones and neurotransmitters.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Edotreotide works by binding to somatostatin receptors that are overexpressed on the surface of certain tumor cells, such as those found in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (GEP-NETs). After binding to these receptors, edotreotide is internalized by the cell, allowing the radioactive component, usually Indium-111 (111In), to accumulate within the tumor. This radioactive labeling enables the visualization of tumors using single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging techniques, providing valuable information about the size, location, and spread of neuroendocrine tumors.
Clinical Uses[edit]
Edotreotide is primarily used in the diagnosis and staging of neuroendocrine tumors. It helps in identifying the presence and extent of the disease, thereby assisting in the planning of appropriate treatment strategies. It is particularly useful in cases where conventional imaging techniques fail to provide clear insights into the tumor's characteristics or when there is a suspicion of metastatic disease.
Side Effects[edit]
The administration of edotreotide is generally well tolerated by patients. However, like all medical procedures and drugs, it may cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects include mild nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Allergic reactions are rare but can occur, necessitating immediate medical attention.
Regulatory Approval[edit]
Edotreotide has been approved by various regulatory bodies, including the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), for use in the diagnostic imaging of neuroendocrine tumors.
Future Directions[edit]
Research is ongoing to explore the potential therapeutic uses of edotreotide, particularly in the treatment of neuroendocrine tumors. Scientists are investigating the possibility of using higher doses of radiation or combining edotreotide with other treatments to enhance its efficacy in tumor reduction or eradication.
-
Edotreotide
-
Yttrium-90 edotreotide
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian