Echinococcus
Echinococcus is a genus of small tapeworms that can cause a disease known as echinococcosis in humans. This disease is characterized by the formation of cysts in various organs of the body, most commonly the liver and lungs.
Overview[edit]
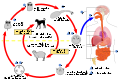
Echinococcus is a genus of tapeworm that belongs to the family Taeniidae. There are four species of Echinococcus that can cause disease in humans: E. granulosus, E. multilocularis, E. vogeli, and E. oligarthrus. These species have a complex life cycle involving two hosts. The adult worms live in the intestines of carnivores, such as dogs or foxes, and the larvae form cysts in various organs of intermediate hosts, such as sheep, cattle, or humans.
Life Cycle[edit]
The life cycle of Echinococcus involves two hosts. The adult worms live in the intestines of the definitive host, where they produce eggs that are passed in the feces. The eggs are ingested by an intermediate host, such as a sheep or a human, and hatch in the intestine to release oncospheres. The oncospheres penetrate the intestinal wall and are carried by the bloodstream to various organs, where they develop into cysts.
Disease[edit]
In humans, infection with Echinococcus can cause a disease known as echinococcosis. This disease is characterized by the formation of cysts in various organs of the body, most commonly the liver and lungs. The cysts can cause various symptoms, depending on their size and location. In some cases, the cysts can rupture and cause severe complications, such as anaphylactic shock.
Diagnosis and Treatment[edit]
Diagnosis of echinococcosis is usually based on imaging studies, such as ultrasound or CT scan, and serological tests. Treatment typically involves surgery to remove the cysts, along with antiparasitic drugs to kill the larvae.
Prevention[edit]
Prevention of echinococcosis involves measures to interrupt the life cycle of the parasite, such as deworming of dogs and proper disposal of animal feces.
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian