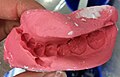
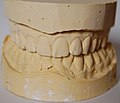
Dental impression
Dental Impression is a procedure in dentistry where an imprint or negative likeness of the teeth and oral tissues is formed. This is used to produce a positive reproduction for the purpose of constructing dental prostheses.
Overview[edit]
A Dental Impression is a representation of the hard and soft tissues of the oral cavity, created from a negative imprint of these structures in a dental impression material. This impression can then be used to create a cast or model of the patient's dentition, which is used in the fabrication of dental restorations, such as crowns, bridges, and dentures.
Procedure[edit]
The process of taking a dental impression involves several steps. First, the dentist selects the appropriate impression tray, which is a device that holds the impression material and is shaped to fit the patient's mouth. The tray is filled with a soft, pliable material, such as alginate or silicone, which hardens after a few minutes to create the impression.
Once the impression material has set, the tray is carefully removed from the patient's mouth, ensuring that the impression is not distorted. The impression is then inspected for accuracy and completeness. If any areas are missing or unclear, the process may need to be repeated.
The dental impression is then sent to a dental laboratory, where it is used to create a detailed model of the patient's teeth and oral tissues. This model serves as a guide for the fabrication of dental restorations.
Types of Dental Impressions[edit]
There are three main types of dental impressions: preliminary, final, and bite registration.
- Preliminary Impressions are used to create diagnostic models for treatment planning and to fabricate custom trays for final impressions.
- Final Impressions are used to produce the precise replica of the oral tissues, which is used in the fabrication of definitive dental restorations.
- Bite Registration Impressions are used to record the relationship between the upper and lower teeth when they are in contact, which is important for the fabrication of occlusal appliances and restorations.
Materials[edit]
Various materials are used in the process of taking dental impressions, including alginate, polyvinyl siloxane, polysulfide, and polyether. The choice of material depends on the specific requirements of the procedure and the preference of the dentist.
Risks and Complications[edit]
While dental impressions are generally safe, there can be potential risks and complications. These may include allergic reactions to the impression materials, discomfort or gagging during the procedure, and inaccuracies in the impression that can lead to ill-fitting restorations.
See Also[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian