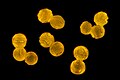
Taraxacum
Article about the genus Taraxacum
Taraxacum is a large genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, which consists of species commonly known as dandelions. The genus is native to Eurasia and North America, but the two most common species worldwide, Taraxacum officinale and Taraxacum erythrospermum, were introduced from Europe and now propagate as wildflowers.
Description[edit]
Taraxacum species are perennial, herbaceous plants that grow from a taproot. They have a rosette of leaves at the base and produce bright yellow flowers. The leaves are deeply lobed and can vary in shape and size. The flowers are composite, consisting of numerous small florets. After flowering, the plant produces a spherical seed head, often referred to as a "dandelion clock," which is composed of many single-seeded fruits called achenes. Each achene is attached to a pappus of fine hairs, which allows it to be carried by the wind.

Ecology[edit]
Taraxacum species are adapted to a wide range of environments and are often found in disturbed habitats such as lawns, roadsides, and fields. They are important early spring nectar sources for pollinators such as bees and butterflies. The seeds are dispersed by wind, which allows them to colonize new areas rapidly.
Uses[edit]
Taraxacum has been used in traditional medicine for centuries. The leaves, flowers, and roots are all edible and have been used in salads, teas, and as a coffee substitute. The plant is rich in vitamins A, C, and K, and contains minerals such as iron, calcium, and potassium.
Medicinal Uses[edit]
Traditionally, dandelion has been used to treat liver disorders, improve digestion, and as a diuretic. Modern research is investigating its potential anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. However, more scientific studies are needed to confirm these health benefits.
Culinary Uses[edit]
The young leaves of Taraxacum can be eaten raw in salads or cooked like spinach. The flowers can be used to make dandelion wine, and the roots can be roasted and ground to make a caffeine-free coffee substitute.

Cultivation[edit]
While often considered a weed, Taraxacum can be cultivated for its edible and medicinal properties. It prefers well-drained soil and full sun but can tolerate partial shade. Regular harvesting of leaves and flowers can prevent the plant from becoming invasive in garden settings.
Also see[edit]

Taraxacum[edit]
-
Dandelion Flower
-
Taraxacum Officinale Seed
-
Dandelion Stigma
-
Pollen Grains of Taraxacum
-
Dandelion Pappus Fiber
-
Floating
-
Желтое море
-
HAWKBEARD
-
Dandelion Seedhead with Only a Single Seed Still Attached
-
T albidum
-
Taraxacum californicum
-
T japonicum
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian