Collective intelligence
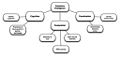
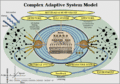
Collective Intelligence refers to the shared or group intelligence that emerges from the collaboration, collective efforts, and competition of many individuals. This phenomenon can be seen in various contexts, including organizations, the internet, animal groups, and other forms of social collaboration. It is a field that intersects with areas such as social psychology, computer science, and information technology, focusing on how groups collectively pool their knowledge and insights to achieve superior outcomes or solve complex problems.
Overview[edit]
Collective intelligence is not a new concept; it has been observed in nature, for example, in ant colonies or bird flocking behavior. However, the advent of the internet and digital communication technologies has greatly enhanced the ability of humans to collaborate and aggregate their cognitive resources on a global scale. This has led to innovative approaches to problem-solving and creativity, exemplified by projects like Wikipedia, open-source software development, and crowdsourcing platforms.
Mechanisms[edit]
The mechanisms underlying collective intelligence include:
- Diversity of Opinion: Each person should have some private information, even if it's just an eccentric interpretation of the known facts.
- Independence: People's opinions are not determined by the opinions of those around them.
- Decentralization: People are able to specialize and draw on local knowledge.
- Aggregation: Some mechanism exists for turning private judgments into a collective decision.
Applications[edit]
Collective intelligence applications span various fields, including:
- Business and Management: Enhancing decision-making, innovation, and problem-solving within organizations.
- Science and Research: Crowdsourcing data collection and analysis to accelerate scientific discoveries.
- Technology Development: Open-source projects and collaborative platforms for software development.
- Education: Collaborative learning environments and platforms that leverage the knowledge of a large group of people.
Challenges and Criticisms[edit]
While collective intelligence can lead to remarkable outcomes, it also faces several challenges, such as:
- Groupthink: The desire for harmony or conformity in the group may result in an irrational or dysfunctional decision-making outcome.
- Information Overload: The sheer volume of information and opinions can be overwhelming and lead to analysis paralysis.
- Quality Control: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the collective output can be challenging, especially in open and decentralized environments.
Future Directions[edit]
The future of collective intelligence lies in enhancing the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies to better aggregate, analyze, and act upon the collective knowledge of humans. This includes developing more sophisticated algorithms for filtering and synthesizing information, as well as creating more intuitive platforms for collaborative work.
See Also[edit]
-
Collective_intelligence
-
Collective_intelligence
-
Collective_intelligence
-
Collective_intelligence
-
Collective_intelligence
-
Collective_intelligence
-
Collective_intelligence
-
Collective_intelligence
-
Collective_intelligence
-
Collective_intelligence
-
Collective_intelligence
-
Collective_intelligence
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian