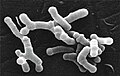
Bifidobacterium longum
Bifidobacterium longum is a species of gram-positive, catalase-negative, rod-shaped bacteria present in the human gastrointestinal tract. It is one of the first bacteria to colonize the sterile digestive tract of newborns and plays a significant role in human health and disease. B. longum is part of the Bifidobacterium genus, which is a major group of probiotic bacteria beneficial for human health. This article provides an overview of Bifidobacterium longum, including its characteristics, health benefits, and applications.
Characteristics[edit]
Bifidobacterium longum is anaerobic, meaning it does not require oxygen to grow. It has a high tolerance to gastric acid, bile, and other digestive substances, allowing it to survive the transit through the stomach and colonize the intestine effectively. B. longum cells are typically elongated, with some strains capable of forming chains. They ferment sugars to produce lactic acid and acetic acid, contributing to the acidic environment of the gut which inhibits the growth of harmful bacteria.
Health Benefits[edit]
B. longum has been associated with numerous health benefits. It is known to:
- Improve gut health by restoring the balance of the intestinal flora, especially after antibiotic therapy.
- Enhance the immune system by stimulating the production of antibodies and promoting the activity of immune cells.
- Reduce the symptoms of certain gastrointestinal disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- Lower the risk of certain infections, including those caused by pathogenic bacteria and viruses.
- Potentially reduce the incidence of allergies by modulating the immune response.
- Aid in the digestion of lactose and prevent lactose intolerance symptoms.
Applications[edit]
B. longum is widely used in the food industry as a probiotic supplement in dairy products, such as yogurt and cheese, as well as in dietary supplements. Its ability to improve gut health and boost the immune system makes it a popular choice for functional foods aimed at promoting health and well-being.
Research[edit]
Research on B. longum continues to uncover its potential benefits and mechanisms of action. Studies have explored its role in reducing anxiety and depression symptoms, its anti-inflammatory properties, and its potential to protect against colon cancer. However, more research is needed to fully understand its health benefits and applications.
Conclusion[edit]
Bifidobacterium longum is a key player in the maintenance of human health through its beneficial effects on the gut microbiota and immune system. Its widespread use in probiotic supplements and functional foods underscores its importance in nutrition and medicine. As research advances, the full potential of B. longum in promoting health and preventing disease may be further realized.
This article is a bacteria-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Bifidobacterium longum en microscopie électronique
-
Representative morphologic characteristics of B. longum subsp. longum strains
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian