Balance theory
Balance Theory is a psychological theory that examines the relationships between individuals and their attitudes towards each other and towards objects or concepts in their environment. Developed by Fritz Heider in the 1940s, it is a part of the broader field of social psychology, focusing on the consistency or balance that individuals strive for in their cognitive systems. The theory is grounded in the idea that people prefer harmonious states and will attempt to change their attitudes to achieve balance within their relationships.
Overview[edit]
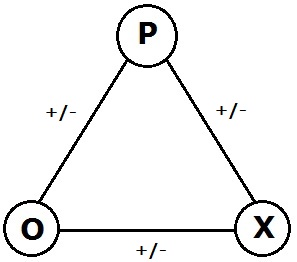
Balance theory is based on the concept of triadic relationships, which involve three entities: the person (P), another person (O), and an impersonal object or concept (X). These relationships can be either balanced or unbalanced, depending on the nature of the attitudes (positive or negative) that link these entities. A balanced state occurs when all three relationships are positive or when two are negative and one is positive, leading to a positive overall sentiment. Conversely, an unbalanced state arises when the combination of attitudes leads to a negative overall sentiment.
Principles[edit]
The core principles of balance theory include:
- Consistency Motive: The drive within individuals to maintain harmony and consistency in their attitudes and beliefs.
- Triadic Relationships: The theory's focus on the dynamics within a triad of entities (P, O, X), which can be people, objects, or concepts.
- Balance and Imbalance: The states of harmony or discord among the attitudes within the triad, with balance being the preferred state.
Applications[edit]
Balance theory has been applied in various fields, including marketing, advertising, and interpersonal relationships. In marketing, for example, it explains how consumers' attitudes towards a product can be influenced by their attitudes towards the advertiser or a celebrity endorser. In interpersonal relationships, it sheds light on how individuals manage their views and interactions to maintain harmony within their social circles.
Criticism and Development[edit]
While balance theory has been influential in understanding attitude change and social dynamics, it has faced criticism for its simplicity and the difficulty of applying its principles to complex real-world situations. Subsequent theories, such as cognitive dissonance theory, have built upon and expanded the concepts introduced by balance theory, offering a more nuanced view of how individuals strive for consistency in their attitudes and beliefs.
See Also[edit]

This article is a psychology-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian