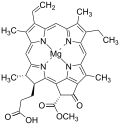
Bacteriochlorophyll
Bacteriochlorophyll refers to a group of photosynthetic pigments found in various photosynthetic bacteria, including purple bacteria and green sulfur bacteria. These pigments are closely related to chlorophyll, which is used by plants, algae, and cyanobacteria to absorb light energy for photosynthesis. However, bacteriochlorophylls are adapted to absorb light in environments with less available sunlight, such as at great depths in water or in sediment, where they can absorb light of wavelengths that are not accessible to chlorophyll.
Structure and Function[edit]
The structure of bacteriochlorophyll molecules is similar to that of chlorophyll, with a central magnesium ion surrounded by a large, complex ring known as a porphyrin. However, bacteriochlorophylls have modifications to this basic structure that allow them to absorb light at different wavelengths. For example, bacteriochlorophyll a, found in purple bacteria, absorbs light in the near-infrared region of the spectrum, around 800 to 900 nm.
Bacteriochlorophylls play a crucial role in the process of photosynthesis in bacteria. They are located in specialized structures called photosynthetic membranes or chlorosomes in some species. These pigments capture light energy and transfer it to reaction centers, where it is used to drive the synthesis of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and reduce NADP+ to NADPH, providing the energy and reducing power needed for carbon fixation.
Types of Bacteriochlorophyll[edit]
There are several types of bacteriochlorophyll, including bacteriochlorophyll a, b, c, d, e, and g, each with a unique absorption spectrum. The distribution of these types varies among different groups of photosynthetic bacteria, contributing to their ability to inhabit diverse ecological niches by utilizing different regions of the light spectrum for photosynthesis.
Ecological and Evolutionary Significance[edit]
Bacteriochlorophyll-containing bacteria are important components of many ecosystems, particularly in anaerobic and low-light environments. By extending the range of light wavelengths that can be used for photosynthesis, these bacteria play a crucial role in the global carbon cycle, contributing to the primary production of organic matter in environments where oxygenic photosynthesizers cannot thrive.
The evolution of bacteriochlorophyll and its associated photosynthetic machinery is of significant interest to scientists studying the origins of photosynthesis. Understanding the diversity and function of bacteriochlorophylls can provide insights into how photosynthesis has adapted to different environmental conditions over geological time scales.
Research and Applications[edit]
Research into bacteriochlorophyll and photosynthetic bacteria has potential applications in renewable energy, such as the development of bio-based solar panels that mimic bacterial photosynthesis. Additionally, bacteriochlorophyll derivatives are being explored for their use in photodynamic therapy, a treatment method for certain types of cancer that involves light-activated drugs.

This article is a photosynthesis stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!

Bacteriochlorophyll[edit]
-
BacterioChlorophyll a
-
Porphyrin, chlorin, bacteriochlorins
-
Chlorophyllide a
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian