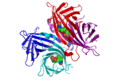
Avidin
Avidin is a tetrameric biotin-binding protein that is produced in the oviducts of birds, reptiles, and amphibians and deposited in the whites of their eggs. In chickens, the most studied source, avidin consists of four identical subunits, each capable of binding biotin (vitamin B7) with a high degree of affinity and specificity. The strong binding of avidin to biotin is exploited in various biotechnological and diagnostic applications, making it a tool of significant interest in the fields of biochemistry and molecular biology.
Structure and Function[edit]
Avidin is a glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 66-69 kDa. Each subunit of avidin is composed of 128 amino acid residues and binds to biotin with a dissociation constant (Kd) in the order of 10^-15 M, which is among the strongest non-covalent interactions known in nature. This high-affinity binding is utilized in affinity chromatography for the purification of biotinylated compounds, among other applications.
The primary function of avidin in nature is thought to be the sequestration of biotin, a vital nutrient, as a defense mechanism against bacteria and fungi in the egg white. The high affinity of avidin for biotin can lead to dietary biotin deficiency if raw egg whites are consumed in large quantities over time, a condition known as "avidin-induced biotin deficiency."
Biotechnological Applications[edit]
Due to its strong binding to biotin, avidin and its derivatives, such as streptavidin and neutravidin, are widely used in biotechnological applications. These include:
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): Avidin-biotin complexes are used to enhance the sensitivity of this assay.
- Western blotting and immunohistochemistry: For the detection of proteins, where biotinylated antibodies are used.
- Affinity chromatography: For the purification of biotinylated molecules.
- Nucleic acid detection: In the labeling and detection of DNA and RNA.
Avidin-Biotin Technology[edit]
The avidin-biotin complex (ABC) technology exploits the high-affinity interaction between avidin and biotin for various applications in life sciences. This technology is used in the detection and quantification of various biomolecules, including proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. The versatility and high sensitivity of ABC technology have made it a valuable tool in research and diagnostic laboratories.
Health Implications[edit]
While avidin's biotin-binding property is beneficial in scientific applications, it can pose health risks when consumed in raw egg whites over prolonged periods. The binding of avidin to biotin in the gastrointestinal tract can prevent the absorption of biotin, leading to deficiency. Cooking egg whites denatures avidin, rendering it unable to bind biotin and mitigating this risk.
See Also[edit]
- Biotin
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- Western blot
- Immunohistochemistry
- Affinity chromatography
References[edit]
<references />

This article is a biochemistry stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Avidin[edit]
-
Tetramer
-
Biotin structure
-
Chicken egg
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian