Analog ear
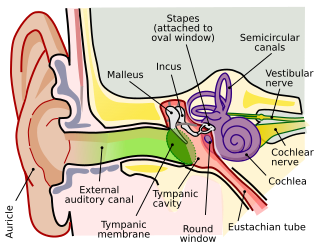
Analog Ear refers to the traditional method of sound processing in hearing aids and other audio devices before the advent of digital technology. Unlike digital hearing aids that convert sound waves into digital signals, analog devices amplify the entire spectrum of sound waves without distinguishing between different types of sounds. This article delves into the components, functionality, and the transition from analog to digital hearing aids.
Components[edit]
An analog ear device primarily consists of a microphone, amplifier, and speaker. The microphone captures sound waves from the environment and converts them into electrical signals. These signals are then amplified by the amplifier based on the settings configured for the user's hearing loss. Finally, the amplified signals are sent to the speaker (or receiver), where they are converted back into sound waves and directed into the ear canal.
Functionality[edit]
The core functionality of an analog hearing aid is to amplify all sounds in the environment. Users can adjust the volume and sometimes the tone to better suit their hearing needs. However, the lack of selective amplification means that background noise is also amplified, making it challenging for the user to focus on specific sounds, like conversations in noisy settings.
Transition to Digital[edit]
The advent of digital technology marked a significant milestone in the evolution of hearing aids. Digital hearing aids convert sound waves into digital signals, allowing for more sophisticated processing. This includes noise reduction, feedback cancellation, and the ability to amplify specific frequencies more than others, tailored to the user's unique hearing loss profile. The transition from analog to digital has greatly improved the user experience, offering clearer sound quality, better speech understanding in noise, and more customization options.
Advantages of Analog Hearing Aids[edit]
Despite the technological advancements of digital hearing aids, analog devices still have their advantages. They are typically simpler to use, with fewer settings and adjustments required. Some users prefer the sound quality of analog hearing aids, describing it as more "natural" compared to the processed sound of digital devices. Additionally, analog hearing aids are often less expensive than their digital counterparts.
Disadvantages[edit]
The main disadvantage of analog hearing aids is their inability to distinguish between different types of sounds. This can make it difficult for users to hear conversations clearly in noisy environments. Additionally, analog devices offer limited customization options, making it challenging to tailor the hearing aid to the specific needs of the user.
Conclusion[edit]
While digital hearing aids have largely replaced analog devices in the market, understanding the principles of analog sound processing is essential for appreciating the advancements in hearing aid technology. Analog hearing aids played a crucial role in the development of assistive hearing devices, providing the foundation upon which modern digital technology has built.
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


