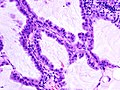
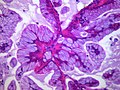
Adenocarcinoma in situ of the lung
| Adenocarcinoma in situ of the lung | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Synonyms | Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Often asymptomatic, cough, shortness of breath |
| Complications | Progression to invasive adenocarcinoma |
| Onset | Typically in older adults |
| Duration | Variable |
| Types | Non-mucinous, mucinous, mixed |
| Causes | Smoking, genetic factors |
| Risks | Smoking, family history of lung cancer |
| Diagnosis | CT scan, biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia, invasive adenocarcinoma |
| Prevention | Smoking cessation, regular screening for high-risk individuals |
| Treatment | Surgical resection, lobectomy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Excellent if completely resected |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Adenocarcinoma in situ of the lung (AIS) is a subtype of lung cancer characterized by the presence of pre-invasive adenocarcinoma cells. It is considered a precursor to invasive adenocarcinoma, which is the most common type of lung cancer. AIS is typically found in the peripheral areas of the lung and is often diagnosed incidentally during imaging studies for other reasons, due to its generally asymptomatic nature in early stages.
Etiology[edit]
The exact cause of AIS is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to genetic mutations in lung cells, which can be triggered by various factors including smoking, exposure to radon gas, asbestos, and other carcinogens. Genetic predisposition may also play a role.
Pathophysiology[edit]
AIS originates in the alveolar epithelial cells, which line the small air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs. These cells begin to proliferate abnormally, forming a localized lesion that does not invade beyond the basement membrane of the epithelium. Without intervention, AIS can progress to invasive adenocarcinoma, which has the potential to spread to other parts of the body.
Clinical Features[edit]
Patients with AIS often do not exhibit symptoms in the early stages. When symptoms do occur, they may include a persistent cough, coughing up blood, shortness of breath, and chest pain. However, these symptoms are not specific to AIS and can be associated with a variety of lung conditions.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of AIS typically involves imaging studies such as CT scans and PET scans, followed by a biopsy to examine the cells under a microscope. Pathological examination is crucial for distinguishing AIS from invasive adenocarcinoma and other types of lung cancer.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment for AIS is primarily surgical resection, which involves removing the affected portion of the lung. This approach is often curative, given the localized nature of the disease. In cases where surgery is not feasible, other treatments such as radiofrequency ablation or stereotactic body radiotherapy may be considered.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for patients with AIS is generally favorable, especially when the condition is diagnosed early and treated promptly. The 5-year survival rate is high, as the disease is typically localized and does not spread to other parts of the body.
Prevention[edit]
Prevention of AIS involves reducing exposure to known risk factors, particularly smoking cessation. Regular medical check-ups and lung cancer screening for high-risk individuals can also aid in early detection and treatment.
Adenocarcinoma in situ of the lung[edit]
-
Adenocarcinoma in situ of the lung
-
Adenocarcinoma in situ of the lung
-
Adenocarcinoma in situ of the lung
-
Adenocarcinoma in situ of the lung
-
Adenocarcinoma in situ of the lung
-
Adenocarcinoma in situ of the lung
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian