Long bone: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:603_Anatomy_of_Long_Bone.jpg|Anatomy of a Long Bone|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Long_bones_-_anterior_view_-_with_legend.png|Long bones - anterior view with legend|left|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Long_bones_-_animation.gif|Long bones animation|thumb]] | |||
A '''[[Long bone]]''' is a type of bone that is significantly longer than it is wide. They are one of the five types of bones in the human body, which also include [[short bone]]s, [[flat bone]]s, [[irregular bone]]s, and [[sesamoid bone]]s. Long bones are found in the limbs and provide support and mobility. | A '''[[Long bone]]''' is a type of bone that is significantly longer than it is wide. They are one of the five types of bones in the human body, which also include [[short bone]]s, [[flat bone]]s, [[irregular bone]]s, and [[sesamoid bone]]s. Long bones are found in the limbs and provide support and mobility. | ||
| Line 19: | Line 20: | ||
Diseases and conditions that can affect long bones include [[osteoporosis]], [[fracture]]s, [[bone cancer]], and [[rickets]]. Treatment options depend on the specific condition and may include medication, surgery, or physical therapy. | Diseases and conditions that can affect long bones include [[osteoporosis]], [[fracture]]s, [[bone cancer]], and [[rickets]]. Treatment options depend on the specific condition and may include medication, surgery, or physical therapy. | ||
== Additional images == | |||
<gallery> | |||
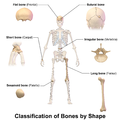
File:Blausen_0229_ClassificationofBones.png|Classification of Bones | |||
File:Blausen_0401_Femur_DistributionofForces.png|Femur Distribution of Forces | |||
File:Os_longum_1.png|Long bone | |||
File:Structure_of_a_Long_Bone.png|Structure of a Long Bone | |||
</gallery> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
* [[Bone marrow]] | * [[Bone marrow]] | ||
| Line 29: | Line 37: | ||
[[Category:Skeletal system]] | [[Category:Skeletal system]] | ||
[[Category:Anatomy]] | [[Category:Anatomy]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 01:04, 7 May 2025



A Long bone is a type of bone that is significantly longer than it is wide. They are one of the five types of bones in the human body, which also include short bones, flat bones, irregular bones, and sesamoid bones. Long bones are found in the limbs and provide support and mobility.
Structure[edit]
Long bones have a tubular shaft, known as the diaphysis, and two rounded ends, known as the epiphysis. The diaphysis is made of compact bone, while the epiphysis is made of spongy bone. The diaphysis contains the medullary cavity, which is filled with bone marrow. The epiphysis is covered with articular cartilage.
Function[edit]
Long bones play a crucial role in the body's movement and support. They serve as levers that are moved by muscles. The length of the bone increases the speed and distance of movement. In addition, the marrow inside the bone produces blood cells.
Development[edit]
Long bones develop through a process called endochondral ossification, which involves the replacement of cartilage with bone. This process begins in the fetus and continues into adolescence.
Clinical significance[edit]
Diseases and conditions that can affect long bones include osteoporosis, fractures, bone cancer, and rickets. Treatment options depend on the specific condition and may include medication, surgery, or physical therapy.
Additional images[edit]
-
Classification of Bones
-
Femur Distribution of Forces
-
Long bone
-
Structure of a Long Bone