Vestibulocerebellar syndrome: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Vestibulocerebellar syndrome | |||
| image = [[File:Gehirn,_basal_-_beschriftet_lat.svg|250px]] | |||
| caption = Basal view of the human brain, showing the cerebellum | |||
| field = [[Neurology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Ataxia]], [[dizziness]], [[nystagmus]], [[vertigo]] | |||
| complications = [[Falls]], [[injury]] | |||
| onset = Varies | |||
| duration = Chronic | |||
| types = [[Congenital]], [[acquired]] | |||
| causes = [[Genetic disorders]], [[stroke]], [[tumors]], [[trauma]] | |||
| risks = [[Family history]], [[head injury]], [[infections]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Clinical examination]], [[MRI]], [[CT scan]] | |||
| differential = [[Multiple sclerosis]], [[inner ear disorders]], [[alcohol intoxication]] | |||
| treatment = [[Physical therapy]], [[medication]], [[surgery]] | |||
| medication = [[Benzodiazepines]], [[antihistamines]] | |||
| prognosis = Variable, depends on cause | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Gray703.png|Diagram of the cerebellum and brainstem|thumb|left]] | |||
[[File:Simple_vestibulo-ocular_reflex.PNG|Illustration of the vestibulo-ocular reflex|thumb|left]] | |||
'''Vestibulocerebellar syndrome''' is a medical condition characterized by a range of symptoms that result from damage or dysfunction of the [[vestibulocerebellum]], a part of the [[brain]] that plays a key role in maintaining balance and coordinating eye movements. | '''Vestibulocerebellar syndrome''' is a medical condition characterized by a range of symptoms that result from damage or dysfunction of the [[vestibulocerebellum]], a part of the [[brain]] that plays a key role in maintaining balance and coordinating eye movements. | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
The symptoms of vestibulocerebellar syndrome can vary widely, but often include: | The symptoms of vestibulocerebellar syndrome can vary widely, but often include: | ||
* [[Dizziness]] | * [[Dizziness]] | ||
* [[Nausea]] | * [[Nausea]] | ||
| Line 12: | Line 31: | ||
* [[Dysarthria]] (difficulty articulating words) | * [[Dysarthria]] (difficulty articulating words) | ||
* [[Dysmetria]] (lack of coordination of movement) | * [[Dysmetria]] (lack of coordination of movement) | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
Vestibulocerebellar syndrome can be caused by a variety of conditions, including: | Vestibulocerebellar syndrome can be caused by a variety of conditions, including: | ||
* [[Stroke]] | * [[Stroke]] | ||
* [[Brain tumor]] | * [[Brain tumor]] | ||
| Line 23: | Line 39: | ||
* [[Vestibular neuritis]] | * [[Vestibular neuritis]] | ||
* [[Meniere's disease]] | * [[Meniere's disease]] | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis of vestibulocerebellar syndrome typically involves a thorough medical history and physical examination, as well as tests to assess balance, coordination, and eye movements. Imaging tests such as [[MRI]] or [[CT scan]] may also be used to identify any abnormalities in the brain. | Diagnosis of vestibulocerebellar syndrome typically involves a thorough medical history and physical examination, as well as tests to assess balance, coordination, and eye movements. Imaging tests such as [[MRI]] or [[CT scan]] may also be used to identify any abnormalities in the brain. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment for vestibulocerebellar syndrome is typically aimed at managing symptoms and treating the underlying cause of the condition. This may involve medication, physical therapy, or in some cases, surgery. | Treatment for vestibulocerebellar syndrome is typically aimed at managing symptoms and treating the underlying cause of the condition. This may involve medication, physical therapy, or in some cases, surgery. | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Cerebellum]] | * [[Cerebellum]] | ||
* [[Vestibular system]] | * [[Vestibular system]] | ||
* [[Neurology]] | * [[Neurology]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Neurological disorders]] | [[Category:Neurological disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Syndromes]] | [[Category:Syndromes]] | ||
[[Category:Medical conditions]] | [[Category:Medical conditions]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 23:55, 9 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Vestibulocerebellar syndrome | |
|---|---|
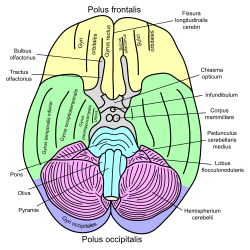
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Ataxia, dizziness, nystagmus, vertigo |
| Complications | Falls, injury |
| Onset | Varies |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | Congenital, acquired |
| Causes | Genetic disorders, stroke, tumors, trauma |
| Risks | Family history, head injury, infections |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination, MRI, CT scan |
| Differential diagnosis | Multiple sclerosis, inner ear disorders, alcohol intoxication |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Physical therapy, medication, surgery |
| Medication | Benzodiazepines, antihistamines |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on cause |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |


Vestibulocerebellar syndrome is a medical condition characterized by a range of symptoms that result from damage or dysfunction of the vestibulocerebellum, a part of the brain that plays a key role in maintaining balance and coordinating eye movements.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of vestibulocerebellar syndrome can vary widely, but often include:
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Nystagmus (involuntary eye movement)
- Ataxia (lack of muscle control or coordination)
- Dysarthria (difficulty articulating words)
- Dysmetria (lack of coordination of movement)
Causes[edit]
Vestibulocerebellar syndrome can be caused by a variety of conditions, including:
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of vestibulocerebellar syndrome typically involves a thorough medical history and physical examination, as well as tests to assess balance, coordination, and eye movements. Imaging tests such as MRI or CT scan may also be used to identify any abnormalities in the brain.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for vestibulocerebellar syndrome is typically aimed at managing symptoms and treating the underlying cause of the condition. This may involve medication, physical therapy, or in some cases, surgery.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />


