Tympanosclerosis: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Tympanosclerosis | |||
| image = [[File:Tympanosclerosis.jpg]] | |||
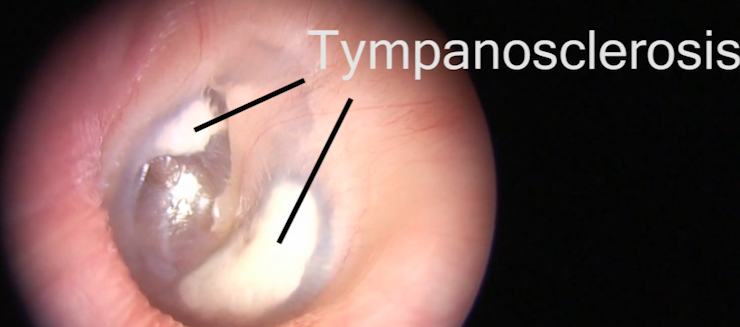
| caption = Tympanosclerosis affecting the tympanic membrane | |||
| field = [[Otorhinolaryngology]] | |||
| synonyms = Myringosclerosis | |||
| symptoms = [[Hearing loss]], [[tinnitus]] | |||
| complications = [[Conductive hearing loss]] | |||
| onset = Variable | |||
| duration = Chronic | |||
| causes = [[Chronic otitis media]], [[ear infections]] | |||
| risks = Recurrent ear infections, [[ear surgery]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Otoscopy]], [[audiometry]] | |||
| differential = [[Otosclerosis]], [[cholesteatoma]] | |||
| prevention = Treating ear infections promptly | |||
| treatment = Hearing aids, [[surgery]] | |||
| medication = None specific | |||
| prognosis = Variable, may lead to permanent hearing loss | |||
| frequency = Common in individuals with chronic ear infections | |||
}} | |||
{{Short description|A condition affecting the tympanic membrane and middle ear}} | {{Short description|A condition affecting the tympanic membrane and middle ear}} | ||
'''Tympanosclerosis''' is a condition characterized by the calcification and scarring of the [[tympanic membrane]] (eardrum) and sometimes the [[middle ear]] structures. It is often associated with chronic [[otitis media]] and can lead to conductive [[hearing loss]]. | '''Tympanosclerosis''' is a condition characterized by the calcification and scarring of the [[tympanic membrane]] (eardrum) and sometimes the [[middle ear]] structures. It is often associated with chronic [[otitis media]] and can lead to conductive [[hearing loss]]. | ||
==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
Tympanosclerosis occurs when there is a deposition of hyaline and calcified plaques in the [[tympanic membrane]] and the [[middle ear]]. This process is thought to be a result of chronic inflammation, often following repeated episodes of [[otitis media]]. The calcification can lead to stiffening of the eardrum and ossicular chain, impairing their ability to transmit sound. | Tympanosclerosis occurs when there is a deposition of hyaline and calcified plaques in the [[tympanic membrane]] and the [[middle ear]]. This process is thought to be a result of chronic inflammation, often following repeated episodes of [[otitis media]]. The calcification can lead to stiffening of the eardrum and ossicular chain, impairing their ability to transmit sound. | ||
==Clinical Presentation== | ==Clinical Presentation== | ||
Patients with tympanosclerosis may present with symptoms of hearing loss, which is typically conductive in nature. The degree of hearing loss can vary depending on the extent of the calcification and involvement of the ossicular chain. Some patients may also experience [[tinnitus]] or a sensation of fullness in the ear. | Patients with tympanosclerosis may present with symptoms of hearing loss, which is typically conductive in nature. The degree of hearing loss can vary depending on the extent of the calcification and involvement of the ossicular chain. Some patients may also experience [[tinnitus]] or a sensation of fullness in the ear. | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Diagnosis of tympanosclerosis is primarily clinical, based on otoscopic examination. The eardrum may appear thickened and opaque, with visible white plaques. Audiometry can be used to assess the degree of hearing loss and to differentiate between conductive and sensorineural components. | Diagnosis of tympanosclerosis is primarily clinical, based on otoscopic examination. The eardrum may appear thickened and opaque, with visible white plaques. Audiometry can be used to assess the degree of hearing loss and to differentiate between conductive and sensorineural components. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment of tympanosclerosis is generally conservative, focusing on managing symptoms. Hearing aids may be used to improve hearing in patients with significant conductive hearing loss. In some cases, surgical intervention, such as [[tympanoplasty]] or ossicular chain reconstruction, may be considered to improve hearing. | Treatment of tympanosclerosis is generally conservative, focusing on managing symptoms. Hearing aids may be used to improve hearing in patients with significant conductive hearing loss. In some cases, surgical intervention, such as [[tympanoplasty]] or ossicular chain reconstruction, may be considered to improve hearing. | ||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
The prognosis for patients with tympanosclerosis varies. While the condition itself is not progressive, the associated hearing loss can impact quality of life. Early intervention and management can help mitigate the effects on hearing. | The prognosis for patients with tympanosclerosis varies. While the condition itself is not progressive, the associated hearing loss can impact quality of life. Early intervention and management can help mitigate the effects on hearing. | ||
==See also== | |||
== | |||
* [[Otitis media]] | * [[Otitis media]] | ||
* [[Hearing loss]] | * [[Hearing loss]] | ||
* [[Tympanic membrane]] | * [[Tympanic membrane]] | ||
* [[Tympanoplasty]] | * [[Tympanoplasty]] | ||
[[Category:Otorhinolaryngology]] | [[Category:Otorhinolaryngology]] | ||
[[Category:Hearing disorders]] | [[Category:Hearing disorders]] | ||
Revision as of 19:36, 8 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Tympanosclerosis | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Myringosclerosis |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Hearing loss, tinnitus |
| Complications | Conductive hearing loss |
| Onset | Variable |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Chronic otitis media, ear infections |
| Risks | Recurrent ear infections, ear surgery |
| Diagnosis | Otoscopy, audiometry |
| Differential diagnosis | Otosclerosis, cholesteatoma |
| Prevention | Treating ear infections promptly |
| Treatment | Hearing aids, surgery |
| Medication | None specific |
| Prognosis | Variable, may lead to permanent hearing loss |
| Frequency | Common in individuals with chronic ear infections |
| Deaths | N/A |
A condition affecting the tympanic membrane and middle ear
Tympanosclerosis is a condition characterized by the calcification and scarring of the tympanic membrane (eardrum) and sometimes the middle ear structures. It is often associated with chronic otitis media and can lead to conductive hearing loss.
Pathophysiology
Tympanosclerosis occurs when there is a deposition of hyaline and calcified plaques in the tympanic membrane and the middle ear. This process is thought to be a result of chronic inflammation, often following repeated episodes of otitis media. The calcification can lead to stiffening of the eardrum and ossicular chain, impairing their ability to transmit sound.
Clinical Presentation
Patients with tympanosclerosis may present with symptoms of hearing loss, which is typically conductive in nature. The degree of hearing loss can vary depending on the extent of the calcification and involvement of the ossicular chain. Some patients may also experience tinnitus or a sensation of fullness in the ear.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of tympanosclerosis is primarily clinical, based on otoscopic examination. The eardrum may appear thickened and opaque, with visible white plaques. Audiometry can be used to assess the degree of hearing loss and to differentiate between conductive and sensorineural components.
Treatment
Treatment of tympanosclerosis is generally conservative, focusing on managing symptoms. Hearing aids may be used to improve hearing in patients with significant conductive hearing loss. In some cases, surgical intervention, such as tympanoplasty or ossicular chain reconstruction, may be considered to improve hearing.
Prognosis
The prognosis for patients with tympanosclerosis varies. While the condition itself is not progressive, the associated hearing loss can impact quality of life. Early intervention and management can help mitigate the effects on hearing.