Syndactyly: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Syndactyly | |||
| image = [[File:Celldeath.jpg|250px]] | |||
| caption = An example of syndactyly | |||
| field = [[Medical genetics]] | |||
| synonyms = Webbed fingers, webbed toes | |||
| symptoms = [[Fused fingers]] or [[toes]] | |||
| complications = Impaired [[hand function]], [[cosmetic]] concerns | |||
| onset = [[Congenital]] | |||
| duration = Lifelong | |||
| causes = [[Genetic mutation]] | |||
| risks = [[Family history]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Physical examination]], [[X-ray]] | |||
| differential = [[Polydactyly]], [[Cleft hand]] | |||
| prevention = None | |||
| treatment = [[Surgery]] | |||
| medication = None | |||
| prognosis = Generally good with treatment | |||
| frequency = 1 in 2,000-3,000 [[births]] | |||
}} | |||
= Syndactyly = | = Syndactyly = | ||
<youtube> | <youtube> | ||
title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | ||
movie_url=http://www.youtube.com/v/_GATUSVnFB0 | movie_url=http://www.youtube.com/v/_GATUSVnFB0 | ||
&rel=1 | &rel=1 | ||
| Line 11: | Line 31: | ||
height=600 | height=600 | ||
</youtube> | </youtube> | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
'''Syndactyly''' is a congenital condition characterized by the fusion of [[fingers]] or toes. It is one of the most common congenital hand anomalies, affecting the development of the digits, leading to them being webbed or joined together. | '''Syndactyly''' is a congenital condition characterized by the fusion of [[fingers]] or toes. It is one of the most common congenital hand anomalies, affecting the development of the digits, leading to them being webbed or joined together. | ||
== Classification == | == Classification == | ||
Syndactyly is classified into several types based on the extent of fusion and the digits involved. The classification system includes simple syndactyly, where only the skin is fused, and complex syndactyly, involving the fusion of bones and other tissues. | Syndactyly is classified into several types based on the extent of fusion and the digits involved. The classification system includes simple syndactyly, where only the skin is fused, and complex syndactyly, involving the fusion of bones and other tissues. | ||
== Causes and Genetics == | == Causes and Genetics == | ||
The exact cause of syndactyly is often unknown, but it can be associated with genetic factors. In some cases, it occurs as part of a genetic syndrome, such as [[Apert Syndrome]] or [[Poland Syndrome]]. | The exact cause of syndactyly is often unknown, but it can be associated with genetic factors. In some cases, it occurs as part of a genetic syndrome, such as [[Apert Syndrome]] or [[Poland Syndrome]]. | ||
== Epidemiology == | == Epidemiology == | ||
Syndactyly can affect anyone but is more commonly seen in males than females. The frequency of occurrence varies among different populations and ethnic groups. | Syndactyly can affect anyone but is more commonly seen in males than females. The frequency of occurrence varies among different populations and ethnic groups. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis is typically made at birth or during a prenatal ultrasound. In more complex cases, imaging studies like X-rays may be required to assess the extent of bone involvement. | Diagnosis is typically made at birth or during a prenatal ultrasound. In more complex cases, imaging studies like X-rays may be required to assess the extent of bone involvement. | ||
== Treatment and Management == | == Treatment and Management == | ||
[[File:Partial Syndactyly 1.jpg|left|thumb|Surgical correction of Syndactyly]] | |||
[[File:Partial Syndactyly 1.jpg|thumb|Surgical correction of Syndactyly]] | |||
Treatment often involves surgical intervention to separate the fused digits. The timing and approach to surgery depend on the severity and type of syndactyly. In cases with minimal fusion, surgery may not be necessary. | Treatment often involves surgical intervention to separate the fused digits. The timing and approach to surgery depend on the severity and type of syndactyly. In cases with minimal fusion, surgery may not be necessary. | ||
== Complications and Prognosis == | == Complications and Prognosis == | ||
While most individuals with syndactyly have normal hand and foot function, complications can include limited range of motion, aesthetic concerns, and, in rare cases, psychosocial impact. | While most individuals with syndactyly have normal hand and foot function, complications can include limited range of motion, aesthetic concerns, and, in rare cases, psychosocial impact. | ||
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
* [[Congenital Anomalies]] | * [[Congenital Anomalies]] | ||
* [[Hand Surgery]] | * [[Hand Surgery]] | ||
* [[Pediatric Orthopedics]] | * [[Pediatric Orthopedics]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
1. [Link to a medical journal article on Syndactyly] | 1. [Link to a medical journal article on Syndactyly] | ||
2. [Link to a health information site with details on Syndactyly] | 2. [Link to a health information site with details on Syndactyly] | ||
== External Links == | == External Links == | ||
* [https://www.orthoinfo.org/en/diseases--conditions/syndactyly/ OrthoInfo - Syndactyly] | * [https://www.orthoinfo.org/en/diseases--conditions/syndactyly/ OrthoInfo - Syndactyly] | ||
* [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430763/ National Center for Biotechnology Information - Syndactyly] | * [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430763/ National Center for Biotechnology Information - Syndactyly] | ||
[[Category:Congenital Disorders]] | [[Category:Congenital Disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Orthopedic Surgical Procedures]] | [[Category:Orthopedic Surgical Procedures]] | ||
[[Category:Pediatrics]] | [[Category:Pediatrics]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:15, 8 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Syndactyly | |
|---|---|
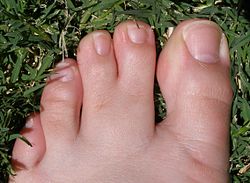
| |
| Synonyms | Webbed fingers, webbed toes |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Fused fingers or toes |
| Complications | Impaired hand function, cosmetic concerns |
| Onset | Congenital |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic mutation |
| Risks | Family history |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, X-ray |
| Differential diagnosis | Polydactyly, Cleft hand |
| Prevention | None |
| Treatment | Surgery |
| Medication | None |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | 1 in 2,000-3,000 births |
| Deaths | N/A |
Syndactyly[edit]
Introduction[edit]
Syndactyly is a congenital condition characterized by the fusion of fingers or toes. It is one of the most common congenital hand anomalies, affecting the development of the digits, leading to them being webbed or joined together.
Classification[edit]
Syndactyly is classified into several types based on the extent of fusion and the digits involved. The classification system includes simple syndactyly, where only the skin is fused, and complex syndactyly, involving the fusion of bones and other tissues.
Causes and Genetics[edit]
The exact cause of syndactyly is often unknown, but it can be associated with genetic factors. In some cases, it occurs as part of a genetic syndrome, such as Apert Syndrome or Poland Syndrome.
Epidemiology[edit]
Syndactyly can affect anyone but is more commonly seen in males than females. The frequency of occurrence varies among different populations and ethnic groups.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis is typically made at birth or during a prenatal ultrasound. In more complex cases, imaging studies like X-rays may be required to assess the extent of bone involvement.
Treatment and Management[edit]

Treatment often involves surgical intervention to separate the fused digits. The timing and approach to surgery depend on the severity and type of syndactyly. In cases with minimal fusion, surgery may not be necessary.
Complications and Prognosis[edit]
While most individuals with syndactyly have normal hand and foot function, complications can include limited range of motion, aesthetic concerns, and, in rare cases, psychosocial impact.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references/> 1. [Link to a medical journal article on Syndactyly] 2. [Link to a health information site with details on Syndactyly]
External Links[edit]
|
|
|

