Medulloblastoma: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Medulloblastoma | {{SI}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Medulloblastoma | |||
| image = [[File:CT_brain_scan_of_child_with_medulloblastoma_and_resulting_hydrocephalus.jpg|250px]] | |||
| caption = CT brain scan of a child with medulloblastoma and resulting hydrocephalus | |||
| field = [[Neuro-oncology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Headache]], [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], [[ataxia]], [[dizziness]], [[vision problems]] | |||
| complications = [[Hydrocephalus]], [[cerebellar mutism syndrome]] | |||
| onset = Most common in children | |||
| duration = Variable | |||
| types = Classic, Desmoplastic/nodular, Large cell/anaplastic, Medulloblastoma with extensive nodularity | |||
| causes = Unknown | |||
| risks = [[Genetic syndromes]] (e.g., [[Gorlin syndrome]], [[Turcot syndrome]]) | |||
| diagnosis = [[MRI]], [[CT scan]], [[biopsy]] | |||
| differential = [[Ependymoma]], [[astrocytoma]], [[brainstem glioma]] | |||
| treatment = [[Surgery]], [[radiation therapy]], [[chemotherapy]] | |||
| prognosis = Variable, depends on age, tumor subtype, and extent of disease | |||
| frequency = Most common malignant brain tumor in children | |||
}} | |||
'''Medulloblastoma''' is a malignant tumor primarily affecting the central nervous system. Though it can manifest in adults, it is predominantly observed in children, making it a significant pediatric concern. | '''Medulloblastoma''' is a malignant tumor primarily affecting the central nervous system. Though it can manifest in adults, it is predominantly observed in children, making it a significant pediatric concern. | ||
[[File:AFIP405851R-MEDULLOBLASTOMA.jpg|left|thumb|250px|MRI scan showing a medulloblastoma.]] | |||
[[File:AFIP405851R-MEDULLOBLASTOMA.jpg|thumb | |||
== Anatomy and Localization == | == Anatomy and Localization == | ||
Medulloblastoma predominantly arises in the cerebellum, an area of the brain responsible for various functions. | Medulloblastoma predominantly arises in the cerebellum, an area of the brain responsible for various functions. | ||
<youtube> | <youtube> | ||
title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | ||
movie_url=http://www.youtube.com/v/sIJAwE0enpo | movie_url=http://www.youtube.com/v/sIJAwE0enpo | ||
&rel=1 | &rel=1 | ||
| Line 19: | Line 32: | ||
height=600 | height=600 | ||
</youtube> | </youtube> | ||
== Cerebellum: The Origin Site == | == Cerebellum: The Origin Site == | ||
* The [[cerebellum]] is situated at the base of the brain and plays a pivotal role in regulating balance, posture, and coordination. | |||
* The [[cerebellum]] is situated at the base of the brain and plays a pivotal role in regulating balance, posture, and coordination. | |||
* Tumors in this area can disrupt these functions, leading to noticeable neurological symptoms. | * Tumors in this area can disrupt these functions, leading to noticeable neurological symptoms. | ||
== Clinical Presentation == | == Clinical Presentation == | ||
Children or adults presenting with medulloblastoma often exhibit certain symptoms that stem from the tumor's location and growth. | Children or adults presenting with medulloblastoma often exhibit certain symptoms that stem from the tumor's location and growth. | ||
* '''Balance and Coordination Issues:''' Due to the cerebellum's function, patients might display challenges with walking or performing coordinated movements. | * '''Balance and Coordination Issues:''' Due to the cerebellum's function, patients might display challenges with walking or performing coordinated movements. | ||
* '''Headaches and Nausea:''' Increased intracranial pressure from tumor growth can lead to persistent headaches and bouts of nausea. | * '''Headaches and Nausea:''' Increased intracranial pressure from tumor growth can lead to persistent headaches and bouts of nausea. | ||
* '''Vision Abnormalities:''' Some patients may experience blurred or double vision. | * '''Vision Abnormalities:''' Some patients may experience blurred or double vision. | ||
== Epidemiology: A Focus on Pediatrics == | == Epidemiology: A Focus on Pediatrics == | ||
While medulloblastomas can be found in individuals of any age, they have a notable prevalence in the pediatric population. | While medulloblastomas can be found in individuals of any age, they have a notable prevalence in the pediatric population. | ||
* '''Age Demographics:''' Most commonly diagnosed in children under the age of 10. | * '''Age Demographics:''' Most commonly diagnosed in children under the age of 10. | ||
* '''Significance:''' It stands as one of the most frequent malignant brain tumors in children. | * '''Significance:''' It stands as one of the most frequent malignant brain tumors in children. | ||
== Diagnosis and Treatment == | == Diagnosis and Treatment == | ||
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for better prognostic outcomes. | Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for better prognostic outcomes. | ||
=== Diagnostic Tools === | === Diagnostic Tools === | ||
* [[MRI]] and [[CT scan]]: These imaging tools are vital in visualizing the tumor. | * [[MRI]] and [[CT scan]]: These imaging tools are vital in visualizing the tumor. | ||
* '''Biopsy:''' A tissue sample helps determine the tumor's exact nature. | * '''Biopsy:''' A tissue sample helps determine the tumor's exact nature. | ||
=== Treatment Modalities === | === Treatment Modalities === | ||
* '''Surgery:''' Removal of the tumor is typically the first line of treatment. | * '''Surgery:''' Removal of the tumor is typically the first line of treatment. | ||
* '''Radiation Therapy:''' Often used post-surgery to target residual cancer cells. | * '''Radiation Therapy:''' Often used post-surgery to target residual cancer cells. | ||
* '''Chemotherapy:''' Employed to kill cancer cells and prevent recurrence. | * '''Chemotherapy:''' Employed to kill cancer cells and prevent recurrence. | ||
== Conclusion == | == Conclusion == | ||
Medulloblastoma, while being a prominent pediatric malignancy, requires comprehensive understanding and multidisciplinary care for effective management. Advancements in research and medical interventions continue to improve the prognosis and quality of life for affected individuals. | Medulloblastoma, while being a prominent pediatric malignancy, requires comprehensive understanding and multidisciplinary care for effective management. Advancements in research and medical interventions continue to improve the prognosis and quality of life for affected individuals. | ||
[[Category:Oncology]] | [[Category:Oncology]] | ||
[[Category:Pediatrics]] | [[Category:Pediatrics]] | ||
[[Category:Neurology]] | [[Category:Neurology]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Revision as of 03:39, 8 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Medulloblastoma | |
|---|---|
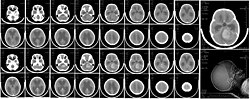
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Headache, nausea, vomiting, ataxia, dizziness, vision problems |
| Complications | Hydrocephalus, cerebellar mutism syndrome |
| Onset | Most common in children |
| Duration | Variable |
| Types | Classic, Desmoplastic/nodular, Large cell/anaplastic, Medulloblastoma with extensive nodularity |
| Causes | Unknown |
| Risks | Genetic syndromes (e.g., Gorlin syndrome, Turcot syndrome) |
| Diagnosis | MRI, CT scan, biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Ependymoma, astrocytoma, brainstem glioma |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on age, tumor subtype, and extent of disease |
| Frequency | Most common malignant brain tumor in children |
| Deaths | N/A |
Medulloblastoma is a malignant tumor primarily affecting the central nervous system. Though it can manifest in adults, it is predominantly observed in children, making it a significant pediatric concern.

Anatomy and Localization
Medulloblastoma predominantly arises in the cerebellum, an area of the brain responsible for various functions.
Cerebellum: The Origin Site
- The cerebellum is situated at the base of the brain and plays a pivotal role in regulating balance, posture, and coordination.
- Tumors in this area can disrupt these functions, leading to noticeable neurological symptoms.
Clinical Presentation
Children or adults presenting with medulloblastoma often exhibit certain symptoms that stem from the tumor's location and growth.
- Balance and Coordination Issues: Due to the cerebellum's function, patients might display challenges with walking or performing coordinated movements.
- Headaches and Nausea: Increased intracranial pressure from tumor growth can lead to persistent headaches and bouts of nausea.
- Vision Abnormalities: Some patients may experience blurred or double vision.
Epidemiology: A Focus on Pediatrics
While medulloblastomas can be found in individuals of any age, they have a notable prevalence in the pediatric population.
- Age Demographics: Most commonly diagnosed in children under the age of 10.
- Significance: It stands as one of the most frequent malignant brain tumors in children.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for better prognostic outcomes.
Diagnostic Tools
- MRI and CT scan: These imaging tools are vital in visualizing the tumor.
- Biopsy: A tissue sample helps determine the tumor's exact nature.
Treatment Modalities
- Surgery: Removal of the tumor is typically the first line of treatment.
- Radiation Therapy: Often used post-surgery to target residual cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Employed to kill cancer cells and prevent recurrence.
Conclusion
Medulloblastoma, while being a prominent pediatric malignancy, requires comprehensive understanding and multidisciplinary care for effective management. Advancements in research and medical interventions continue to improve the prognosis and quality of life for affected individuals.


