Hyperalgesia: Difference between revisions
From WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Hyperalgesia | |||
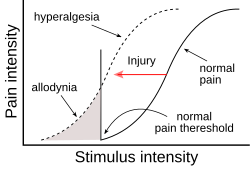
| image = [[File:Hyperalgesia_and_allodynia.svg|250px]] | |||
| caption = Diagram illustrating hyperalgesia and allodynia | |||
| field = [[Neurology]] | |||
| symptoms = Increased sensitivity to pain | |||
| causes = [[Nerve injury]], [[inflammation]], [[opioid]] use | |||
| diagnosis = [[Clinical diagnosis]] | |||
| differential = [[Allodynia]], [[neuropathic pain]] | |||
| treatment = [[Analgesics]], [[antidepressants]], [[anticonvulsants]] | |||
| frequency = Common in patients with chronic pain conditions | |||
}} | |||
'''Hyperalgesia''' is an increased sensitivity to pain, which may be caused by damage to nociceptors or peripheral nerves. Temporary increased sensitivity to pain also occurs as part of the body's defense mechanisms during illness or injury. | '''Hyperalgesia''' is an increased sensitivity to pain, which may be caused by damage to nociceptors or peripheral nerves. Temporary increased sensitivity to pain also occurs as part of the body's defense mechanisms during illness or injury. | ||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
Hyperalgesia can be caused by a number of factors, including: | Hyperalgesia can be caused by a number of factors, including: | ||
| Line 7: | Line 19: | ||
* Certain medications, such as opioids | * Certain medications, such as opioids | ||
* Certain diseases, such as [[fibromyalgia]] and [[migraines]] | * Certain diseases, such as [[fibromyalgia]] and [[migraines]] | ||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
The main symptom of hyperalgesia is an unusually strong reaction to painful stimuli. This can include: | The main symptom of hyperalgesia is an unusually strong reaction to painful stimuli. This can include: | ||
| Line 13: | Line 24: | ||
* Pain from stimuli that do not normally cause pain (allodynia) | * Pain from stimuli that do not normally cause pain (allodynia) | ||
* Increased pain from stimuli that are far from the area of injury or inflammation (secondary hyperalgesia) | * Increased pain from stimuli that are far from the area of injury or inflammation (secondary hyperalgesia) | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment for hyperalgesia focuses on managing the underlying cause of the increased pain sensitivity. This can include: | Treatment for hyperalgesia focuses on managing the underlying cause of the increased pain sensitivity. This can include: | ||
| Line 19: | Line 29: | ||
* Physical therapy to help manage pain and improve function | * Physical therapy to help manage pain and improve function | ||
* Psychological therapies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy, to help manage the emotional impact of chronic pain | * Psychological therapies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy, to help manage the emotional impact of chronic pain | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
* [[Allodynia]] | * [[Allodynia]] | ||
* [[Pain management]] | * [[Pain management]] | ||
* [[Chronic pain]] | * [[Chronic pain]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
[[Category:Medical conditions]] | [[Category:Medical conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Pain]] | [[Category:Pain]] | ||
[[Category:Neurology]] | [[Category:Neurology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:33, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Hyperalgesia | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Increased sensitivity to pain |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | N/A |
| Duration | N/A |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Nerve injury, inflammation, opioid use |
| Risks | N/A |
| Diagnosis | Clinical diagnosis |
| Differential diagnosis | Allodynia, neuropathic pain |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Analgesics, antidepressants, anticonvulsants |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | Common in patients with chronic pain conditions |
| Deaths | N/A |
Hyperalgesia is an increased sensitivity to pain, which may be caused by damage to nociceptors or peripheral nerves. Temporary increased sensitivity to pain also occurs as part of the body's defense mechanisms during illness or injury.
Causes[edit]
Hyperalgesia can be caused by a number of factors, including:
- Inflammation or injury to the skin or other tissues
- Nerve damage or irritation
- Certain medications, such as opioids
- Certain diseases, such as fibromyalgia and migraines
Symptoms[edit]
The main symptom of hyperalgesia is an unusually strong reaction to painful stimuli. This can include:
- Increased pain from stimuli that normally cause pain
- Pain from stimuli that do not normally cause pain (allodynia)
- Increased pain from stimuli that are far from the area of injury or inflammation (secondary hyperalgesia)
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for hyperalgesia focuses on managing the underlying cause of the increased pain sensitivity. This can include:
- Medications to reduce inflammation and pain
- Physical therapy to help manage pain and improve function
- Psychological therapies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy, to help manage the emotional impact of chronic pain
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />


