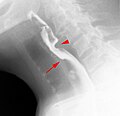
Esophageal web: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Esophageal web | |||
| image = [[File:Esophageal_web.jpg]] | |||
| caption = Endoscopic image of an esophageal web | |||
| field = [[Gastroenterology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Dysphagia]], [[odynophagia]], [[iron deficiency anemia]] | |||
| complications = [[Esophageal cancer]] | |||
| onset = Any age, more common in adults | |||
| duration = Chronic | |||
| causes = [[Plummer-Vinson syndrome]], [[congenital]] | |||
| risks = [[Iron deficiency]], [[autoimmune disorders]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Barium swallow]], [[endoscopy]] | |||
| differential = [[Esophageal stricture]], [[esophageal ring]] | |||
| treatment = [[Endoscopic dilation]], [[iron supplementation]] | |||
| prognosis = Good with treatment | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
{{jpg-image}} | {{jpg-image}} | ||
'''Esophageal web''' is a thin, membrane-like tissue growth that occurs in the esophagus. It is a rare condition that can cause difficulty swallowing and other symptoms. | '''Esophageal web''' is a thin, membrane-like tissue growth that occurs in the esophagus. It is a rare condition that can cause difficulty swallowing and other symptoms. | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
The exact cause of esophageal web is unknown. However, it is often associated with certain conditions such as [[iron deficiency anemia]], [[Plummer-Vinson syndrome]], and [[celiac disease]]. | The exact cause of esophageal web is unknown. However, it is often associated with certain conditions such as [[iron deficiency anemia]], [[Plummer-Vinson syndrome]], and [[celiac disease]]. | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
The most common symptom of esophageal web is difficulty swallowing, also known as [[dysphagia]]. Other symptoms may include pain or discomfort in the chest, weight loss, and regurgitation of food. | The most common symptom of esophageal web is difficulty swallowing, also known as [[dysphagia]]. Other symptoms may include pain or discomfort in the chest, weight loss, and regurgitation of food. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Esophageal web is typically diagnosed through a procedure called an [[endoscopy]], where a thin tube with a camera is inserted down the throat to examine the esophagus. Other diagnostic tests may include a [[barium swallow]] or an [[esophagram]]. | Esophageal web is typically diagnosed through a procedure called an [[endoscopy]], where a thin tube with a camera is inserted down the throat to examine the esophagus. Other diagnostic tests may include a [[barium swallow]] or an [[esophagram]]. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment for esophageal web often involves a procedure to stretch or remove the web. This can be done through an endoscopy or a surgical procedure. In some cases, treatment for the underlying condition, such as iron supplementation for iron deficiency anemia, may also be necessary. | Treatment for esophageal web often involves a procedure to stretch or remove the web. This can be done through an endoscopy or a surgical procedure. In some cases, treatment for the underlying condition, such as iron supplementation for iron deficiency anemia, may also be necessary. | ||
== Esophageal web images == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Zervikales Web.jpg|Zervikales Web | |||
File:Web mit Jet-Phaenomen.jpg|Web mit Jet-Phaenomen | |||
File:Zervikales Web pa.jpg|Zervikales Web pa | |||
</gallery> | |||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Esophageal stricture]] | * [[Esophageal stricture]] | ||
* [[Esophageal cancer]] | * [[Esophageal cancer]] | ||
* [[Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)]] | * [[Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
[[Category:Gastroenterology]] | [[Category:Gastroenterology]] | ||
[[Category:Esophagus]] | [[Category:Esophagus]] | ||
[[Category:Medical conditions]] | [[Category:Medical conditions]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:14, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Esophageal web | |
|---|---|
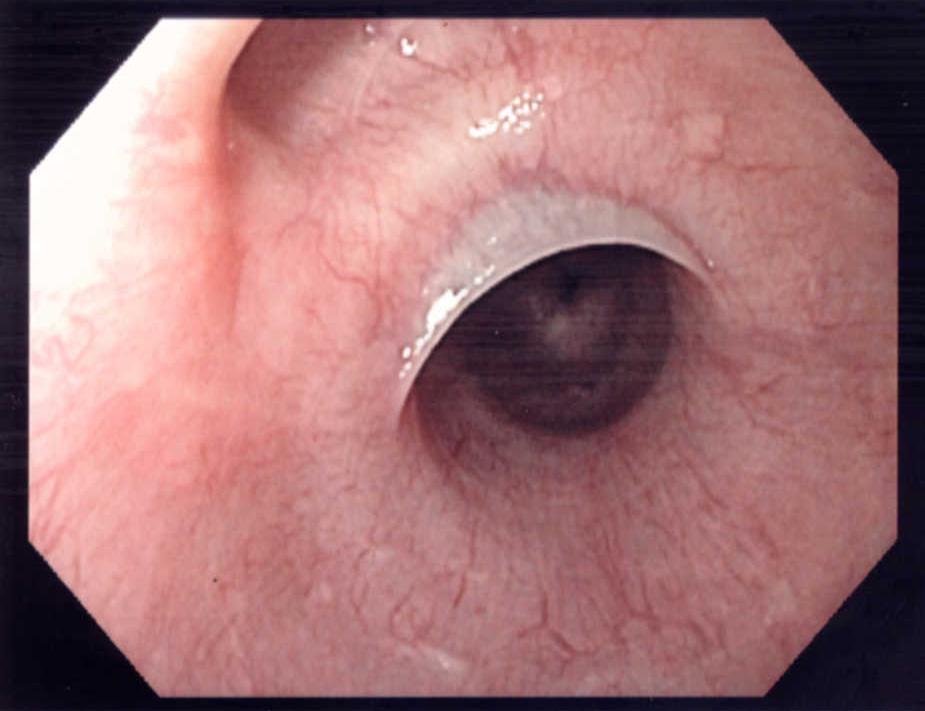
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Dysphagia, odynophagia, iron deficiency anemia |
| Complications | Esophageal cancer |
| Onset | Any age, more common in adults |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Plummer-Vinson syndrome, congenital |
| Risks | Iron deficiency, autoimmune disorders |
| Diagnosis | Barium swallow, endoscopy |
| Differential diagnosis | Esophageal stricture, esophageal ring |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Endoscopic dilation, iron supplementation |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Good with treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |

Esophageal web is a thin, membrane-like tissue growth that occurs in the esophagus. It is a rare condition that can cause difficulty swallowing and other symptoms.
Causes[edit]
The exact cause of esophageal web is unknown. However, it is often associated with certain conditions such as iron deficiency anemia, Plummer-Vinson syndrome, and celiac disease.
Symptoms[edit]
The most common symptom of esophageal web is difficulty swallowing, also known as dysphagia. Other symptoms may include pain or discomfort in the chest, weight loss, and regurgitation of food.
Diagnosis[edit]
Esophageal web is typically diagnosed through a procedure called an endoscopy, where a thin tube with a camera is inserted down the throat to examine the esophagus. Other diagnostic tests may include a barium swallow or an esophagram.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for esophageal web often involves a procedure to stretch or remove the web. This can be done through an endoscopy or a surgical procedure. In some cases, treatment for the underlying condition, such as iron supplementation for iron deficiency anemia, may also be necessary.
Esophageal web images[edit]
-
Zervikales Web
-
Web mit Jet-Phaenomen
-
Zervikales Web pa
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />