Post-traumatic amnesia: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Post-traumatic amnesia | |||
| image = [[File:Headscratcher.png|alt=Confused person scratching head]] | |||
| caption = A depiction of confusion, a common symptom of post-traumatic amnesia | |||
| field = [[Neurology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Memory loss]], [[disorientation]], [[confusion]] | |||
| onset = Immediately after [[traumatic brain injury]] | |||
| duration = Minutes to weeks, depending on severity | |||
| causes = [[Traumatic brain injury]] | |||
| risks = [[Motor vehicle accidents]], [[falls]], [[sports injuries]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Clinical assessment]], [[Glasgow Coma Scale]], [[neuropsychological testing]] | |||
| differential = [[Concussion]], [[dementia]], [[delirium]] | |||
| treatment = [[Supportive care]], [[rehabilitation]], [[cognitive therapy]] | |||
| prognosis = Varies; can be full recovery or persistent memory issues | |||
| frequency = Common in [[traumatic brain injury]] cases | |||
}} | |||
'''Post-traumatic amnesia''' ('''PTA''') is a state of confusion that occurs immediately following a [[traumatic brain injury]] (TBI) in which the injured person is disoriented and unable to remember events that occur after the injury. The person may be unable to state their name, where they are, and what time it is. When continuous memory returns, PTA is considered to have resolved. While PTA lasts, new events cannot be stored in the memory. | '''Post-traumatic amnesia''' ('''PTA''') is a state of confusion that occurs immediately following a [[traumatic brain injury]] (TBI) in which the injured person is disoriented and unable to remember events that occur after the injury. The person may be unable to state their name, where they are, and what time it is. When continuous memory returns, PTA is considered to have resolved. While PTA lasts, new events cannot be stored in the memory. | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
PTA is caused by a [[traumatic brain injury]], such as a blow to the head. The length of time that PTA lasts can be an indicator of the severity of the brain injury. The longer the duration of amnesia, the more severe the injury is likely to be. | PTA is caused by a [[traumatic brain injury]], such as a blow to the head. The length of time that PTA lasts can be an indicator of the severity of the brain injury. The longer the duration of amnesia, the more severe the injury is likely to be. | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
The main symptom of PTA is memory loss. This can be loss of memory for events before the injury ([[retrograde amnesia]]), or events after the injury ([[anterograde amnesia]]). Other symptoms can include confusion, disorientation, and agitation. | The main symptom of PTA is memory loss. This can be loss of memory for events before the injury ([[retrograde amnesia]]), or events after the injury ([[anterograde amnesia]]). Other symptoms can include confusion, disorientation, and agitation. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis of PTA is based on clinical assessment of the patient's ability to consistently form new memories. This is often done using the [[Galveston Orientation and Amnesia Test]] (GOAT), which assesses orientation to person, place, and time, and the ability to remember events since the injury. | Diagnosis of PTA is based on clinical assessment of the patient's ability to consistently form new memories. This is often done using the [[Galveston Orientation and Amnesia Test]] (GOAT), which assesses orientation to person, place, and time, and the ability to remember events since the injury. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment for PTA involves supportive care and rehabilitation. This can include [[occupational therapy]] to help the person manage daily activities, and [[cognitive rehabilitation]] to improve memory and other cognitive functions. | Treatment for PTA involves supportive care and rehabilitation. This can include [[occupational therapy]] to help the person manage daily activities, and [[cognitive rehabilitation]] to improve memory and other cognitive functions. | ||
== Prognosis == | == Prognosis == | ||
The prognosis for PTA depends on the severity of the brain injury. Most people with mild to moderate injuries recover fully, but those with severe injuries may have long-term problems with memory and cognition. | The prognosis for PTA depends on the severity of the brain injury. Most people with mild to moderate injuries recover fully, but those with severe injuries may have long-term problems with memory and cognition. | ||
==Post-traumatic_amnesia images== | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Hippocampus.gif|Hippocampus | |||
File:Arginine_vasopressin3d.png|Arginine vasopressin 3D model | |||
File:Shellshock2.jpg|Shell shock | |||
File:Elderly_Woman,_B&W_image_by_Chalmers_Butterfield.jpg|Elderly Woman | |||
</gallery> | |||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Traumatic brain injury]] | * [[Traumatic brain injury]] | ||
| Line 21: | Line 39: | ||
* [[Retrograde amnesia]] | * [[Retrograde amnesia]] | ||
* [[Anterograde amnesia]] | * [[Anterograde amnesia]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Neurological disorders]] | [[Category:Neurological disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Memory disorders]] | [[Category:Memory disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Amnesia]] | [[Category:Amnesia]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 05:29, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Post-traumatic amnesia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Memory loss, disorientation, confusion |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Immediately after traumatic brain injury |
| Duration | Minutes to weeks, depending on severity |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Traumatic brain injury |
| Risks | Motor vehicle accidents, falls, sports injuries |
| Diagnosis | Clinical assessment, Glasgow Coma Scale, neuropsychological testing |
| Differential diagnosis | Concussion, dementia, delirium |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Supportive care, rehabilitation, cognitive therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies; can be full recovery or persistent memory issues |
| Frequency | Common in traumatic brain injury cases |
| Deaths | N/A |
Post-traumatic amnesia (PTA) is a state of confusion that occurs immediately following a traumatic brain injury (TBI) in which the injured person is disoriented and unable to remember events that occur after the injury. The person may be unable to state their name, where they are, and what time it is. When continuous memory returns, PTA is considered to have resolved. While PTA lasts, new events cannot be stored in the memory.
Causes[edit]
PTA is caused by a traumatic brain injury, such as a blow to the head. The length of time that PTA lasts can be an indicator of the severity of the brain injury. The longer the duration of amnesia, the more severe the injury is likely to be.
Symptoms[edit]
The main symptom of PTA is memory loss. This can be loss of memory for events before the injury (retrograde amnesia), or events after the injury (anterograde amnesia). Other symptoms can include confusion, disorientation, and agitation.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of PTA is based on clinical assessment of the patient's ability to consistently form new memories. This is often done using the Galveston Orientation and Amnesia Test (GOAT), which assesses orientation to person, place, and time, and the ability to remember events since the injury.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for PTA involves supportive care and rehabilitation. This can include occupational therapy to help the person manage daily activities, and cognitive rehabilitation to improve memory and other cognitive functions.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for PTA depends on the severity of the brain injury. Most people with mild to moderate injuries recover fully, but those with severe injuries may have long-term problems with memory and cognition.
Post-traumatic_amnesia images[edit]
-
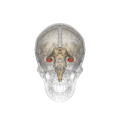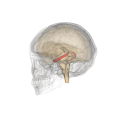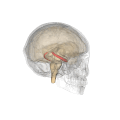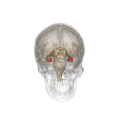
Hippocampus
-
Arginine vasopressin 3D model
-
Shell shock
-
Elderly Woman
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />