Ape hand deformity: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
File:Ape_Hand.jpg| | {{Infobox medical condition | ||
File:Apehand_1.JPG|Ape hand deformity | | name = Ape hand deformity | ||
File:Apehand_2.JPG|Ape hand deformity | | image = [[File:Ape_Hand.jpg|250px]] | ||
| caption = Illustration of ape hand deformity | |||
| synonyms = Simian hand | |||
| specialty = [[Neurology]], [[Orthopedics]] | |||
| symptoms = Inability to oppose the thumb, flattening of the thenar eminence | |||
| causes = [[Median nerve]] injury | |||
| risks = [[Carpal tunnel syndrome]], [[trauma]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Physical examination]], [[Electromyography]] | |||
| treatment = [[Surgery]], [[physical therapy]] | |||
| prognosis = Varies depending on cause and treatment | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Apehand_1.JPG|Ape hand deformity|left|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Apehand_2.JPG|Ape hand deformity|left|thumb]] | |||
'''Ape hand deformity''' is a condition characterized by the inability to oppose the thumb to the other fingers, resulting in a hand posture that resembles that of an ape. This condition is primarily associated with [[median nerve]] dysfunction, which affects the [[thenar eminence]] muscles responsible for thumb opposition. | '''Ape hand deformity''' is a condition characterized by the inability to oppose the thumb to the other fingers, resulting in a hand posture that resembles that of an ape. This condition is primarily associated with [[median nerve]] dysfunction, which affects the [[thenar eminence]] muscles responsible for thumb opposition. | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
Ape hand deformity is most commonly caused by injury or compression of the median nerve. This can occur due to: | Ape hand deformity is most commonly caused by injury or compression of the median nerve. This can occur due to: | ||
* [[Carpal tunnel syndrome]] | * [[Carpal tunnel syndrome]] | ||
* [[Trauma]] to the wrist or forearm | * [[Trauma]] to the wrist or forearm | ||
| Line 17: | Line 24: | ||
* [[Brachial plexus injury]] | * [[Brachial plexus injury]] | ||
* [[Tumors]] or [[cysts]] compressing the nerve | * [[Tumors]] or [[cysts]] compressing the nerve | ||
== Pathophysiology == | == Pathophysiology == | ||
The median nerve innervates the thenar muscles, including the [[opponens pollicis]], [[abductor pollicis brevis]], and [[flexor pollicis brevis]]. These muscles are responsible for the opposition and flexion of the thumb. When the median nerve is compromised, these muscles become weak or paralyzed, leading to the characteristic posture of the thumb in ape hand deformity. | The median nerve innervates the thenar muscles, including the [[opponens pollicis]], [[abductor pollicis brevis]], and [[flexor pollicis brevis]]. These muscles are responsible for the opposition and flexion of the thumb. When the median nerve is compromised, these muscles become weak or paralyzed, leading to the characteristic posture of the thumb in ape hand deformity. | ||
== Clinical Presentation == | == Clinical Presentation == | ||
Patients with ape hand deformity typically present with: | Patients with ape hand deformity typically present with: | ||
* Inability to oppose the thumb | * Inability to oppose the thumb | ||
* Flattening of the thenar eminence | * Flattening of the thenar eminence | ||
* Weakness in thumb flexion and abduction | * Weakness in thumb flexion and abduction | ||
* Sensory loss in the lateral three and a half fingers | * Sensory loss in the lateral three and a half fingers | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis of ape hand deformity involves: | Diagnosis of ape hand deformity involves: | ||
* Clinical examination to assess thumb opposition and thenar muscle function | * Clinical examination to assess thumb opposition and thenar muscle function | ||
* [[Electromyography]] (EMG) and [[nerve conduction studies]] to evaluate median nerve function | * [[Electromyography]] (EMG) and [[nerve conduction studies]] to evaluate median nerve function | ||
* Imaging studies such as [[MRI]] or [[ultrasound]] to identify structural causes of nerve compression | * Imaging studies such as [[MRI]] or [[ultrasound]] to identify structural causes of nerve compression | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment of ape hand deformity depends on the underlying cause and may include: | Treatment of ape hand deformity depends on the underlying cause and may include: | ||
* [[Physical therapy]] to strengthen hand muscles and improve function | * [[Physical therapy]] to strengthen hand muscles and improve function | ||
* [[Splinting]] to support the thumb and improve hand posture | * [[Splinting]] to support the thumb and improve hand posture | ||
* Surgical intervention to relieve nerve compression or repair nerve damage | * Surgical intervention to relieve nerve compression or repair nerve damage | ||
* [[Occupational therapy]] to assist with adaptive techniques for daily activities | * [[Occupational therapy]] to assist with adaptive techniques for daily activities | ||
== Prognosis == | == Prognosis == | ||
The prognosis for ape hand deformity varies depending on the cause and severity of the nerve injury. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes, but severe or prolonged nerve damage may result in permanent dysfunction. | The prognosis for ape hand deformity varies depending on the cause and severity of the nerve injury. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes, but severe or prolonged nerve damage may result in permanent dysfunction. | ||
== See Also == | |||
== | |||
* [[Median nerve]] | * [[Median nerve]] | ||
* [[Carpal tunnel syndrome]] | * [[Carpal tunnel syndrome]] | ||
* [[Peripheral neuropathy]] | * [[Peripheral neuropathy]] | ||
* [[Brachial plexus injury]] | * [[Brachial plexus injury]] | ||
{{Hand deformities}} | {{Hand deformities}} | ||
[[Category:Musculoskeletal disorders]] | [[Category:Musculoskeletal disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Neurological disorders]] | [[Category:Neurological disorders]] | ||
Latest revision as of 22:26, 5 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Ape hand deformity | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | Simian hand |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Neurology, Orthopedics |
| Symptoms | Inability to oppose the thumb, flattening of the thenar eminence |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | N/A |
| Duration | N/A |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Median nerve injury |
| Risks | Carpal tunnel syndrome, trauma |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, Electromyography |
| Differential diagnosis | N/A |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgery, physical therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies depending on cause and treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |

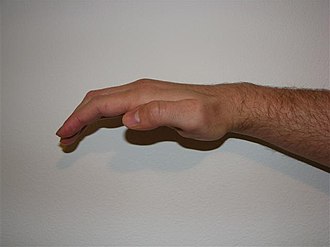
Ape hand deformity is a condition characterized by the inability to oppose the thumb to the other fingers, resulting in a hand posture that resembles that of an ape. This condition is primarily associated with median nerve dysfunction, which affects the thenar eminence muscles responsible for thumb opposition.
Causes[edit]
Ape hand deformity is most commonly caused by injury or compression of the median nerve. This can occur due to:
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Trauma to the wrist or forearm
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Brachial plexus injury
- Tumors or cysts compressing the nerve
Pathophysiology[edit]
The median nerve innervates the thenar muscles, including the opponens pollicis, abductor pollicis brevis, and flexor pollicis brevis. These muscles are responsible for the opposition and flexion of the thumb. When the median nerve is compromised, these muscles become weak or paralyzed, leading to the characteristic posture of the thumb in ape hand deformity.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
Patients with ape hand deformity typically present with:
- Inability to oppose the thumb
- Flattening of the thenar eminence
- Weakness in thumb flexion and abduction
- Sensory loss in the lateral three and a half fingers
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of ape hand deformity involves:
- Clinical examination to assess thumb opposition and thenar muscle function
- Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies to evaluate median nerve function
- Imaging studies such as MRI or ultrasound to identify structural causes of nerve compression
Treatment[edit]
Treatment of ape hand deformity depends on the underlying cause and may include:
- Physical therapy to strengthen hand muscles and improve function
- Splinting to support the thumb and improve hand posture
- Surgical intervention to relieve nerve compression or repair nerve damage
- Occupational therapy to assist with adaptive techniques for daily activities
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for ape hand deformity varies depending on the cause and severity of the nerve injury. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes, but severe or prolonged nerve damage may result in permanent dysfunction.