Ductal carcinoma in situ: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Ductal carcinoma in situ''' ('''DCIS''') is a non-invasive form of [[breast cancer]] where abnormal cells have been found in the lining of the breast milk duct. The atypical cells have not spread outside of the ducts into the surrounding breast tissue. Ductal Carcinoma In Situ is very early cancer that is highly treatable, but if | {{SI}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Ductal carcinoma in situ | |||
| image = [[File:Lobules_and_ducts_of_the_breast.jpg|250px]] | |||
| caption = Diagram showing the [[lobules]] and [[ducts]] of the [[breast]] | |||
| field = [[Oncology]] | |||
| synonyms = DCIS | |||
| symptoms = Usually none, sometimes a [[breast lump]] or [[nipple discharge]] | |||
| complications = [[Invasive breast cancer]] | |||
| onset = Typically after age 50 | |||
| duration = Variable | |||
| types = [[Comedo]], [[non-comedo]] | |||
| causes = [[Genetic mutations]], [[hormonal factors]] | |||
| risks = [[Family history]], [[BRCA1]]/[[BRCA2]] mutations, [[hormone replacement therapy]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Mammography]], [[biopsy]] | |||
| differential = [[Invasive ductal carcinoma]], [[lobular carcinoma in situ]] | |||
| prevention = [[Regular screening]], [[lifestyle modifications]] | |||
| treatment = [[Surgery]], [[radiation therapy]], [[hormonal therapy]] | |||
| prognosis = Excellent with treatment | |||
| frequency = Common in women over 50 | |||
}} | |||
'''Ductal carcinoma in situ''' ('''DCIS''') is a non-invasive form of [[breast cancer]] where abnormal cells have been found in the lining of the breast milk duct. The atypical cells have not spread outside of the ducts into the surrounding breast tissue. Ductal Carcinoma In Situ is very early cancer that is highly treatable, but if it’s left untreated or undetected, it can spread into the surrounding breast tissue. | |||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
DCIS itself does not cause symptoms. It is often detected during a [[mammogram]] as part of a regular screening program. | DCIS itself does not cause symptoms. It is often detected during a [[mammogram]] as part of a regular screening program. | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
The exact cause of DCIS is unknown. However, it is known that cancer arises when a cell's DNA is damaged. Factors that may increase your risk of DCIS include age, a personal history of benign (noncancerous) breast disease, a family history of breast cancer, inherited genes that increase the risk of breast cancer, radiation exposure, and hormone therapy. | The exact cause of DCIS is unknown. However, it is known that cancer arises when a cell's DNA is damaged. Factors that may increase your risk of DCIS include age, a personal history of benign (noncancerous) breast disease, a family history of breast cancer, inherited genes that increase the risk of breast cancer, radiation exposure, and hormone therapy. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
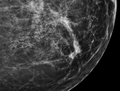
DCIS is usually found during a mammogram done as part of a routine screening program. If an abnormal area is seen on the mammogram, a biopsy may be done to check for cancer cells. | DCIS is usually found during a mammogram done as part of a routine screening program. If an abnormal area is seen on the mammogram, a biopsy may be done to check for cancer cells. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment options for DCIS include [[lumpectomy]] in combination with radiation therapy, [[mastectomy]], and hormone therapy. | Treatment options for DCIS include [[lumpectomy]] in combination with radiation therapy, [[mastectomy]], and hormone therapy. | ||
== Prognosis == | == Prognosis == | ||
The prognosis for DCIS is generally very good. Since DCIS is a non-invasive cancer, it is highly treatable. However, it is important to have regular check-ups after treatment to ensure that the cancer has not returned or spread. | The prognosis for DCIS is generally very good. Since DCIS is a non-invasive cancer, it is highly treatable. However, it is important to have regular check-ups after treatment to ensure that the cancer has not returned or spread. | ||
== Gallery == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Breast DCIS histopathology (1).jpg|Breast DCIS histopathology | |||
File:Diagram showing ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) CRUK 115.svg|Diagram showing ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) | |||
File:Nci-vol-4353-300 ductal carcinoma in situ.jpg|Ductal carcinoma in situ | |||
File:Mammogram microcalcifications in carcinoma in situ, CC, details.png|Mammogram microcalcifications in carcinoma in situ | |||
File:Histopathology of dystrophic microcalcifications in ductal carcinoma in situ.jpg|Histopathology of dystrophic microcalcifications in ductal carcinoma in situ | |||
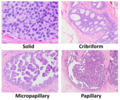
File:Histopathologic architectural patterns of DCIS.png|Histopathologic architectural patterns of DCIS | |||
File:Histopathology of high-grade DCIS.png|Histopathology of high-grade DCIS | |||
File:Histopathology of microinvasive ductal carcinoma in situ.png|Histopathology of microinvasive ductal carcinoma in situ | |||
File:Immunohistochemistry with calponin in ductal carcinoma in situ.jpg|Immunohistochemistry with calponin in ductal carcinoma in situ | |||
File:Histopathology of ductal carcinoma in situ with comedo necrosis.jpg|Histopathology of ductal carcinoma in situ with comedo necrosis | |||
File:Pie chart of incidence and prognosis of histopathologic breast cancer types.png|Pie chart of incidence and prognosis of histopathologic breast cancer types | |||
</gallery> | |||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Breast cancer]] | * [[Breast cancer]] | ||
| Line 22: | Line 51: | ||
* [[Mastectomy]] | * [[Mastectomy]] | ||
* [[Hormone therapy]] | * [[Hormone therapy]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Breast cancer]] | [[Category:Breast cancer]] | ||
[[Category:Cancer]] | [[Category:Cancer]] | ||
[[Category:Medical conditions]] | [[Category:Medical conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Oncology]] | [[Category:Oncology]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 19:24, 5 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Ductal carcinoma in situ | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | DCIS |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Usually none, sometimes a breast lump or nipple discharge |
| Complications | Invasive breast cancer |
| Onset | Typically after age 50 |
| Duration | Variable |
| Types | Comedo, non-comedo |
| Causes | Genetic mutations, hormonal factors |
| Risks | Family history, BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations, hormone replacement therapy |
| Diagnosis | Mammography, biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Invasive ductal carcinoma, lobular carcinoma in situ |
| Prevention | Regular screening, lifestyle modifications |
| Treatment | Surgery, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Excellent with treatment |
| Frequency | Common in women over 50 |
| Deaths | N/A |
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a non-invasive form of breast cancer where abnormal cells have been found in the lining of the breast milk duct. The atypical cells have not spread outside of the ducts into the surrounding breast tissue. Ductal Carcinoma In Situ is very early cancer that is highly treatable, but if it’s left untreated or undetected, it can spread into the surrounding breast tissue.
Symptoms[edit]
DCIS itself does not cause symptoms. It is often detected during a mammogram as part of a regular screening program.
Causes[edit]
The exact cause of DCIS is unknown. However, it is known that cancer arises when a cell's DNA is damaged. Factors that may increase your risk of DCIS include age, a personal history of benign (noncancerous) breast disease, a family history of breast cancer, inherited genes that increase the risk of breast cancer, radiation exposure, and hormone therapy.
Diagnosis[edit]
DCIS is usually found during a mammogram done as part of a routine screening program. If an abnormal area is seen on the mammogram, a biopsy may be done to check for cancer cells.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment options for DCIS include lumpectomy in combination with radiation therapy, mastectomy, and hormone therapy.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for DCIS is generally very good. Since DCIS is a non-invasive cancer, it is highly treatable. However, it is important to have regular check-ups after treatment to ensure that the cancer has not returned or spread.
Gallery[edit]
-
Breast DCIS histopathology
-
Diagram showing ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
-
Ductal carcinoma in situ
-
Mammogram microcalcifications in carcinoma in situ
-
Histopathology of dystrophic microcalcifications in ductal carcinoma in situ
-
Histopathologic architectural patterns of DCIS
-
Histopathology of high-grade DCIS
-
Histopathology of microinvasive ductal carcinoma in situ
-
Immunohistochemistry with calponin in ductal carcinoma in situ
-
Histopathology of ductal carcinoma in situ with comedo necrosis
-
Pie chart of incidence and prognosis of histopathologic breast cancer types
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />